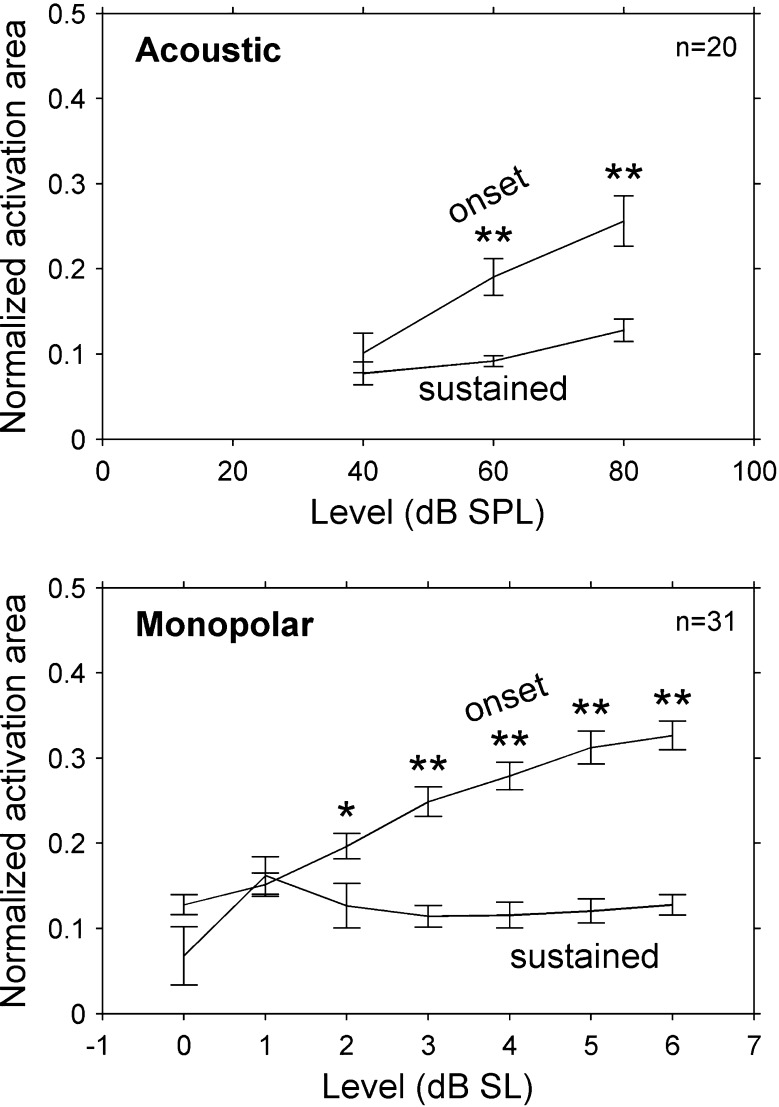
FIG. 15.
Normalized activation area was smaller for the sustained time window than for the onset time window in cats. This effect increased with stimulus level, indicating that at higher levels the shape of the sustained response was narrower than that of the onset response (even for normalized peak spike rates). Values are means and error bars are standard errors of the means. Acoustic data are from 20 stimulus frequencies in two cats. Monopolar data are from 31 stimulus channels in eight cats. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001 relative to sustained area.