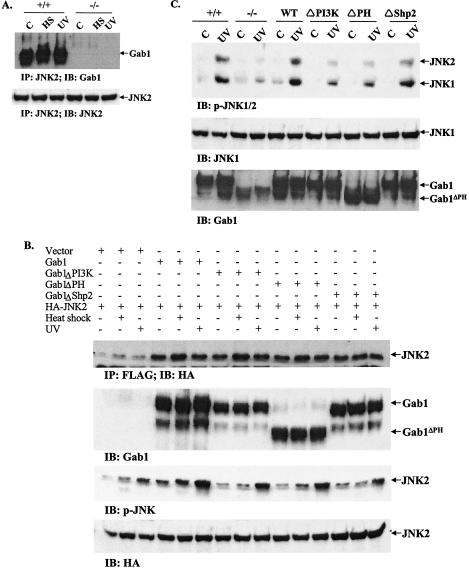
FIG. 4.
Signaling from Gab1 to JNK. (A). Association of Gab1 with JNK2 in fibroblast cells. Wild-type (+/+) and Gab1−/− (−/−) cells were heat shocked (HS) at 42°C for 1 h or irradiated with UV-B light (400 J/m2) and then incubated at 37°C for 1 h. Cell lysates were prepared and subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with an anti-JNK2 antibody. The immunoprecipitates were resolved by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and immunoblotted (IB) with an anti-Gab1 antibody. The membrane was then stripped and reprobed with an anti-JNK2 antibody. (B) Association of Gab1 mutants with JNK2. COS1 cells in 100-mm plates were cotransfected in triplicate with 2 μg of HA-JNK2 and 2 μg each of Gab1 constructs or pcDNA3.1 as indicated. Transfected cells were heat shocked at 42°C for 1 h or irradiated with UV-B light at 400 J/m2. Expression of JNK2 and Gab1 were detected by immunoblotting with anti-HA and anti-Gab1 antibodies, respectively. Association of Gab1 and JNK2 was demonstrated by immunoprecipitation of cell lystates with an anti-Flag antibody and immunoblotting with an anti-HA antibody. Activation of JNK was examined using a p-JNK antibody. (C) Rescue of defective JNK activation by wild-type and mutant Gab1. Gab1−/− fibroblast cells were transiently transfected with Flag tagged-human Gab1 and different mutants and then subjected to heat shock (42°C for 1 h) or UV-B irradiation at 400 J/m2. JNK activation was detected by immunoblotting using an anti-p-JNK antibody. Expression of exogenous Gab1 was shown by anti-Gab1 immunoblotting.