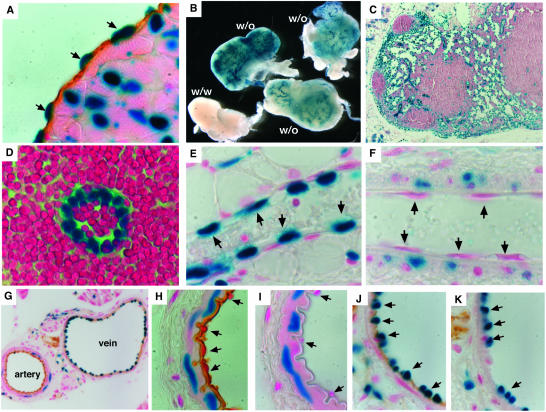
FIG. 5.
β-Galactosidase assay for bik expression. (A) bik expression in endocardium, confirmed by combined staining for β-galactosidase activity (blue) and immunohistochemical staining for CD31 (brown). (B) Whole-mount β-galactosidase staining of lymph nodes from bik+/− mice demonstrating bik expression in lymphoid vasculature. (C and D) The identity of β-galactosidase-positive cells in lymph nodes was determined as endothelium by morphology from thin sections of whole-mount stained nodes. (E and F) Thin sections from whole-mount β-galactosidase-stained mammary gland venule (E) and arteriole (F). Arrows indicate representative endothelial cells. (G) Combination of β-galactosidase staining and immunohistochemical staining for CD31 on frozen sections of blood vessels from the pancreas of bik+/− animals. (H to K) High-power images showing the morphology of the artery (H and I) and vein (J and K) and the distribution of β-galactosidase staining. Anti-B220 antibody staining (I and K) is included as an isotype-matched control for the anti-CD31 antibody (H and J). Arrows indicate representative endothelial cells. In no case was β-galactosidase staining observed in the above-mentioned cell types from wt animals.