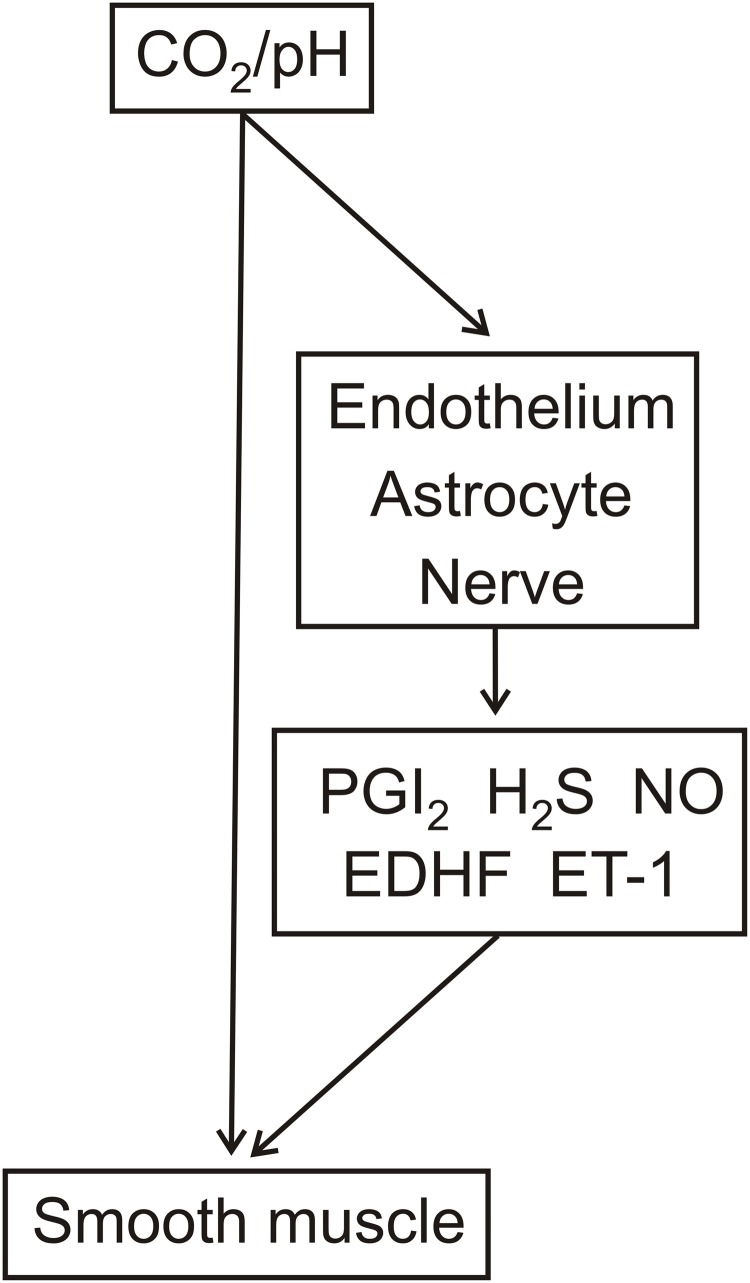
Figure 2.
Potential cellular sites of action and vasoactive factor involvement in respiratory hypercapnia/hypocapnia-mediated relaxation/contraction. The effects of respiratory hypercapnia/hypocapnia may be mediated through accompanying changes in pH and/or directly by pCO2. pH and/or pCO2 act on the smooth muscle as well as on the endothelium, nerves, and astrocytes. These latter cell types release vasoactive factors, including PGI2, H2S, NO, endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor (EDHF), and endothelin-1 (ET-1).