Figure 2.
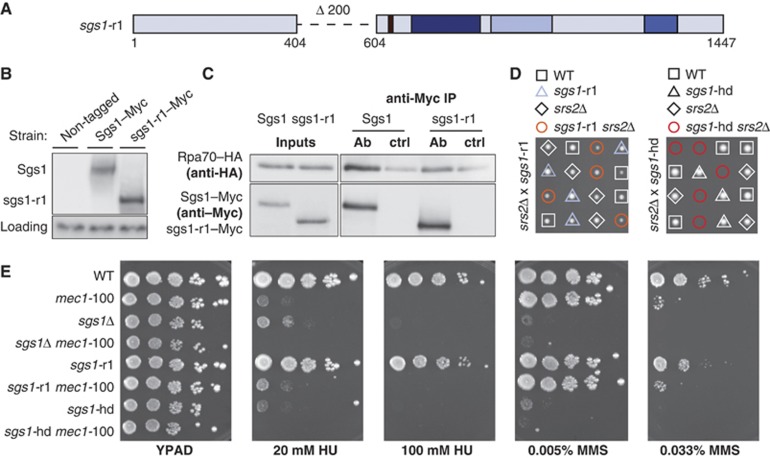
Loss of the acidic region in Sgs1 impairs Sgs1–RPA interaction in vivo. (A) Schematic representation of sgs1-r1: a new allele generated by deleting the acidic region (aa 404–604) at the endogenous SGS1 locus. The deleted region is indicated by a dashed line. Black=acidic block, dark blue=helicase domain, light blue=RQC domain, blue=HRDC domain. (B) Wild type and sgs1-r1 were C-terminally fused to 13Myc epitopes at the endogenous SGS1 locus (Sgs1–13Myc; GA-5311, sgs1-r1–13Myc; GA-5313) and expression levels were analysed by western blot with anti-Myc antibody. Non-tagged strain (GA-7249) was used as a negative control. Anti-actin was used to detect Act1 as a loading control. (C) Co-IP of exponentially growing 13Myc-tagged Sgs1 (GA-1759) or sgs1-r1 (GA-5316) with 3HA-tagged Rpa70. Exponentially growing cells were collected for IP using Dynabeads either coupled to monoclonal anti-Myc (AB) or not (ctrl). Western blots were probed with anti-Myc (9E10) for Sgs1 or sgs1-r1 and anti-HA (F-7) for Rpa70. (D) sgs1-r1 (GA-4848) and srs2Δ (GA-1805), as well as sgs1-hd (GA-5445) and srs2Δ (GA-5334) mutants were crossed and sporulated and tetrad analysis was performed. (E) Ten-fold serial dilutions of the following strains were plated onto YPAD, ±20 mM or 100 mM HU, 0.005% or 0.033% MMS: GA-1981 (WT), GA-4978 (mec1-100), GA-5457 (sgs1Δ), GA-4967 (sgs1Δ mec1-100), GA-5076 (sgs1-r1), GA-5077 (sgs1-r1 mec1-100), GA-5445 (sgs1-hd) and GA-5447 (sgs1-hd mec1-100).