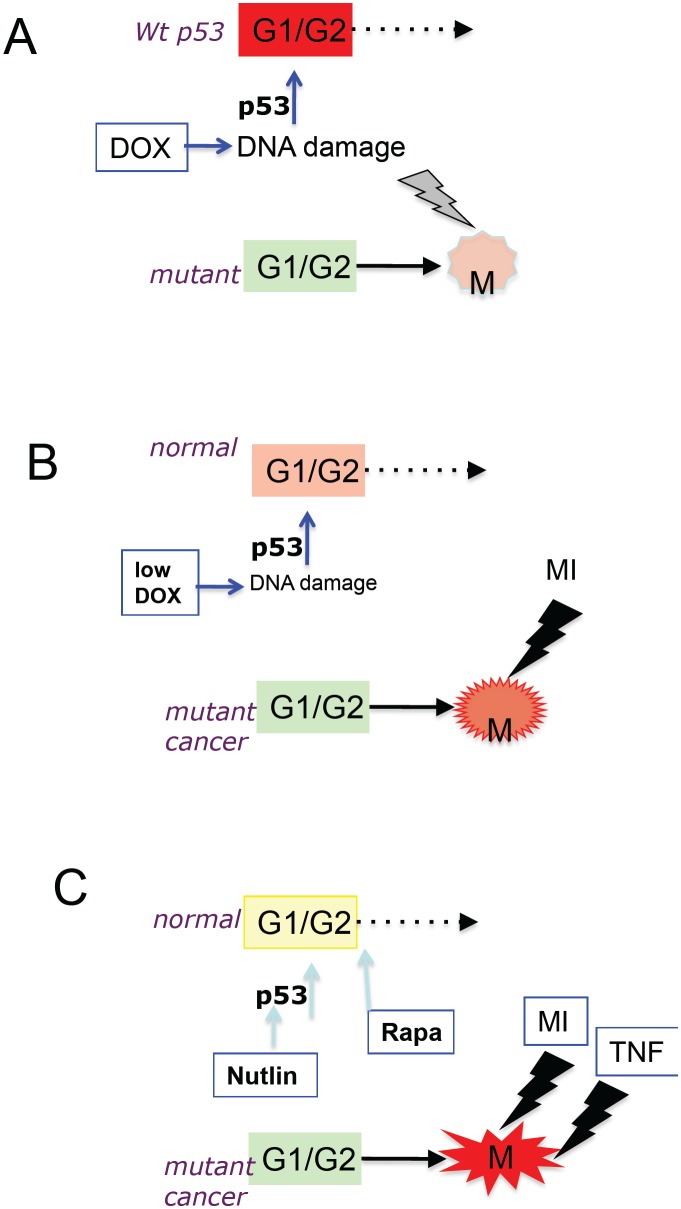
Figure 1. Protection of normal cells: From a single drug to ordered combinations.
(A) Doxorubicin (Dox) causes G1/G2 arrest (red) in wt p53 cells, whereas cancer cells with mutant p53 enter mitosis (M) and undergo mitotic catastrophe. (B) Low doses of doxorubicin (low DOX) cause a more gentle G1/G2 arrest (orange) in normal cells, whereas cancer cells with mutant p53 enter mitosis (M) and are killed by MI (mitotic inhibitor such as Taxol). (C) Nutlin-3a plus rapamycin cause the gentlest G1/G2 arrest (yellow) in normal cells, whereas cancer cells with mutant p53 enter mitosis (M) and are killed by a highly apoptotic combination of MI plus TRAIL or TNF.