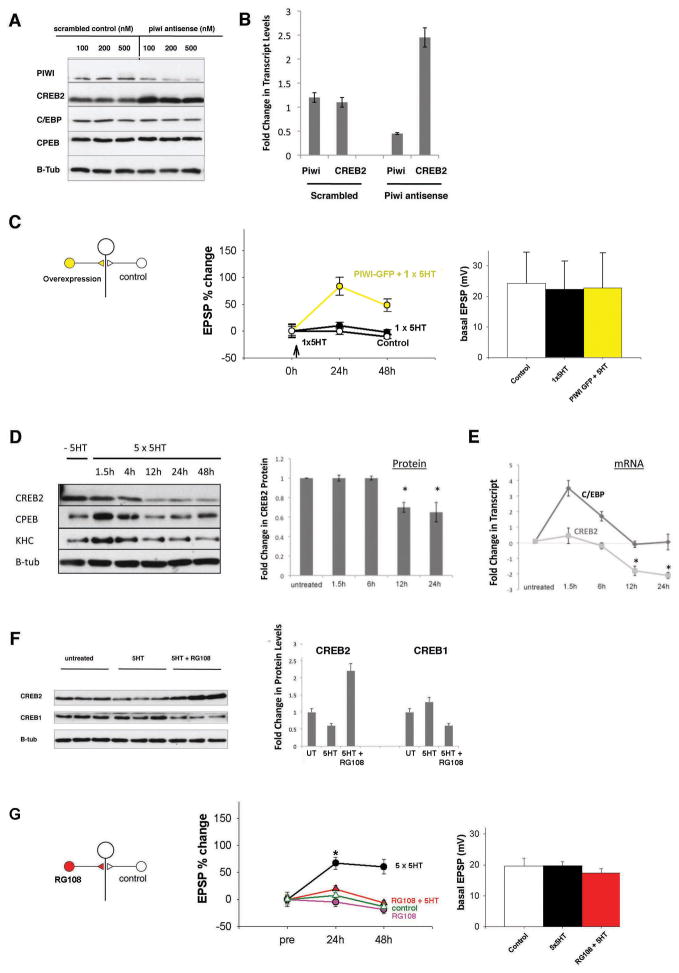
Figure 4.
A. Knockdown of piwi causes a robust up-regulation of CREB2, which is specific as there is no significant change in expression levels of C/EBP or CPEB (effects quantified as a mean of 4 independent trials ± S.D).
B. Real Time PCR experiments show that knockdown of piwi produces a significant increase in CREB2 RNA levels, when normalized to GAPDH levels.
C. Electrophysiology experiment reporting percentage change in EPSP amplitude measured at 24 h and 48 h after 1×5HT with respect to pre-treatment values for neurons over-expressing piwi-GFP, as compared to control cells. The effects observed were not due to changes in the baseline strength of piwi-GFP versus control synapses.
D. Aplysia sensory neurons were either treated with vehicle or 5HT and protein was subsequently extracted at 1.5, 4, 12, 24, and 48 hours after 5HT. CREB2, CPEB, and KHC levels were monitored. Blots were re-probed for tubulin to control for equal loading of samples. This exact time course was run only once, but a similar time course is shown quantified in the next panel as a mean of 3 independent trials ± S.D.
E. Real time PCR experiments showing that CREB2 RNA levels have a long-lasting and more robust down-regulation after exposure to 5HT. The 5HT-dependent early induction of C/EBP mRNA (a known immediate early gene) from the same preparation is shown as a positive control.
F. Three independent experiments each, of neurons treated with vehicle, 5HT, or 5HT in the presence of a DNA methyltransferase inhibitor (RG108) are shown where the proteins were extracted 12 h later and western blotted. CREB2 is down-regulated by 5HT, and this effect is reversed in the presence of RG108. The opposite is observed for CREB1.
G. Electrophysiology experiment reporting percentage change in EPSP amplitude measured at 24 h and 48 h after 5×5HT with respect to pre-treatment values for neurons treated with RG108, as compared to control population. The inhibitor was confirmed to not be toxic to the cells as application of the inhibitor alone in the absence of 5HT had no effect on the baseline strength of the synapses.