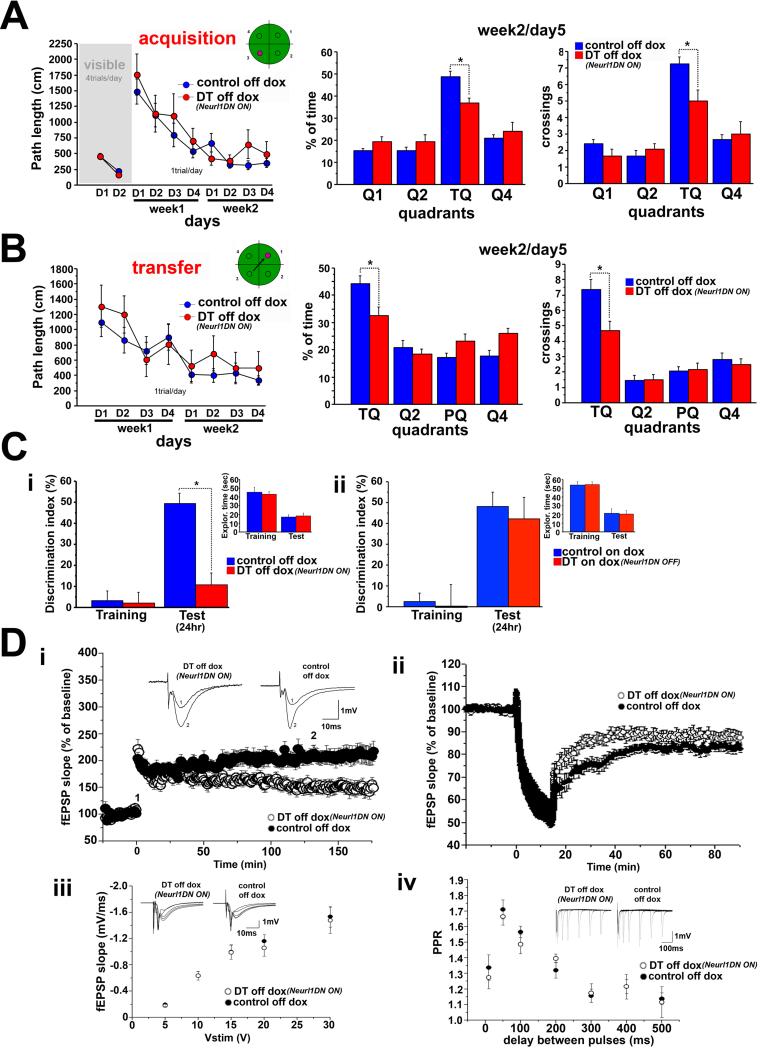
Figure 2. Inhibition of Neurl1 in the adult hippocampus impairs memory and synaptic plasticity.
(A) Averaged data (+SEM) from the Morris water maze of Neurl1DN expressing mice (DT off dox) and control siblings. The performance of DT was significantly lower in the probe trial (quadrant*genotype effect: p<0.04, t-test for training quadrant (TQ): *p<0.007).
(B) Transfer phase of the water maze. DT performed significantly worse than controls in the probe trial (quadrant*genotype effect: p<0.04, t test for TQ, *p<0.013). PQ: TQ in A.
(C) Novel object recognition (mean +SEM). (i) The discrimination index of DT was significantly lower in the 24hr test (*p=0.001). Total exploration times were similar (p>0.4). (ii) Mice tested on dox. No differences were observed (p>0.6).
(D) Expression of Neurl1DN in the hippocampus impairs the late phase of LTP and LTD at the Schaeffer collateral pathway. (i) LTP induction was not affected in DT (t-test 0-60min: p=0.17). L-LTP was impaired (t-test 60-120min & 120-180min; p<0.02) Insets: example of 10 averaged traces before (1) and after (2) LTP induction. (ii) LTD was impaired in DT (t-test 40-90 min: p<0.05). Basal transmission (iii) and paired-pulse facilitation (iv) were unaltered (ANOVA; p>0.63). Insets in (iii) & (iv): sample traces (PPR: traces for 10, 50, 100, 200 & 300 ms delays between pulses).