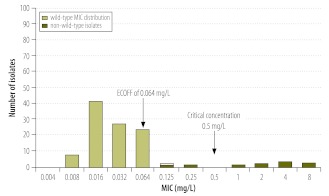
Fig. 3.
Wild-type minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) distribution for rifabutin
ECOFF, epidemiological cut-off.
Note: The non-wild-type isolates were non wild-type for rifampicin and had mutations associated with resistance in the rpoB gene.13 Thus, the present critical concentration of 0.5 mg/L for Middlebrook 7H10 medium (indicated by an arrow) is probably set too high by at least two twofold dilution steps, which has led to the belief, not supported by clinical evidence, that some strains resistant to rifampicin are susceptible to rifabutin.
Reproduced with permission from the International Union Against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease.