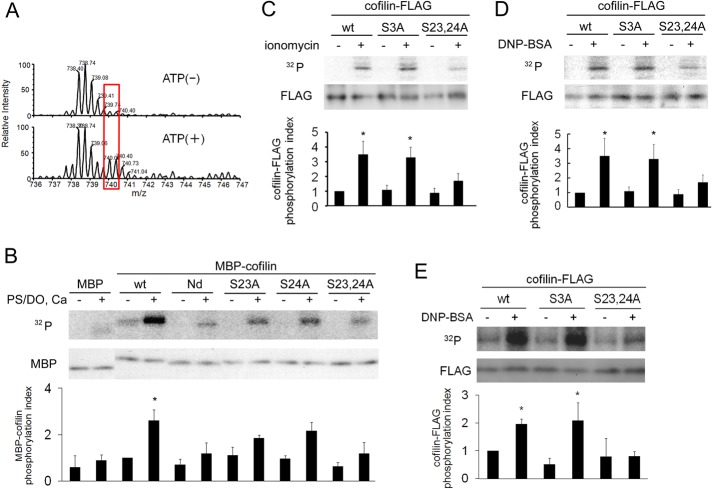
FIGURE 4:
Determination of the PKCα phosphorylation site(s) in cofilin. (A) Mass spectrometric analysis of cofilin phosphorylated by purified PKCα in vitro. Purified MBP-cofilin was incubated with PKCα in the presence or absence of ATP, Ca2+, and PS/DO at 30°C for 15 min. After separation by SDS–PAGE, MBP-cofilin was subjected to mass spectrometry. The detected mass values for untreated (top) and ATP-treated cofilin (bottom) are shown. Spectra that were dependent on the presence of ATP are indicated by red boxes. The first peak is mono isotopic and the second is isotopic; detailed data are shown in Supplemental Figure S8. (B) In vitro phosphorylation of cofilin at Ser-23 and/or Ser-24 by PKCα. An in vitro kinase assay was performed with purified PKCα and MBP-cofilin wild-type (WT), the N-terminal–deletion mutant (Nd; lacking the N-terminal 24 amino acids), and the serine mutants (S3A, S23A, S24A, S23,24A) in the presence (+) or absence (–) of PKC activators. (C, D) The in vivo phosphorylation of cofilin at Ser-23 and Ser-24 during degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells. Plasmids of FLAG-tagged wild-type cofilin or the S3A, or S23,24A mutants were transfected into RBL-2H3 cells and then stimulated with 1 μM ionomycin (C) or 50 ng/ml DNP-BSA (D). (E) The in vivo phosphorylation of cofilin at Ser-23 and Ser-24 during degranulation in mouse BMMC. Plasmids of FLAG-tagged wild-type cofilin or the S3A or S23,24A mutants were transfected into BMMC cells and then stimulated with 1 μM ionomycin. Quantitative analysis of cofilin phosphorylation from three independent experiments is shown in the bottom graphs of B– E; bars represent SD. Quantification was performed by normalizing the radioactive bands in the kinase assay to the total amount of cofilin (*p < 0.05).