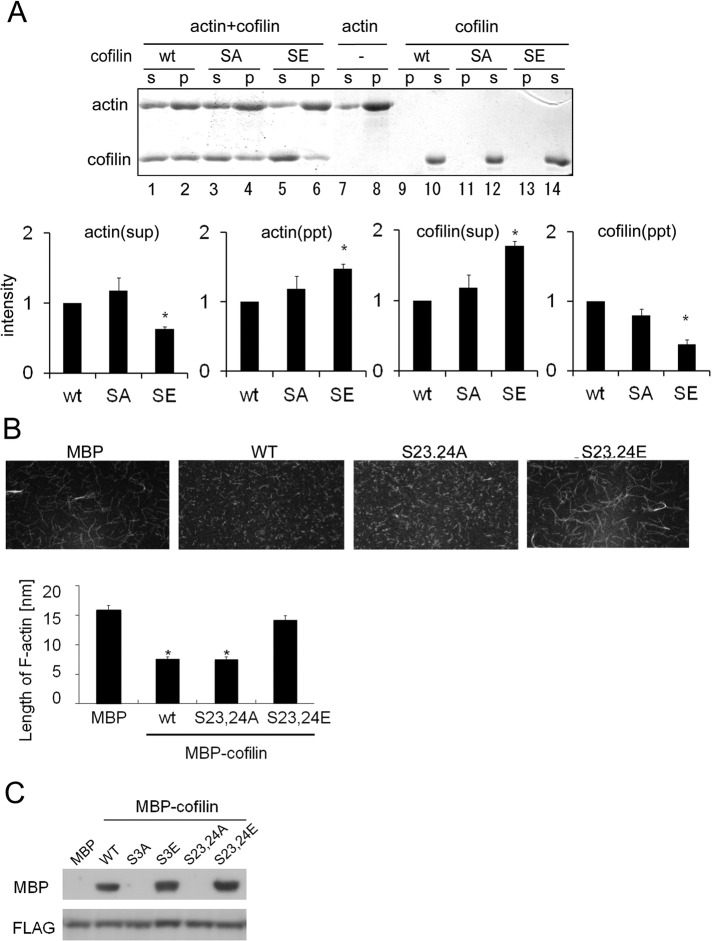
FIGURE 6:
Cofilin phosphorylation at Ser-23 and Ser-24 influences depolymerization of F-actin and binding to 14-3-3ζ. (A) The F-actin sedimentation assay. Purified wild-type (WT) cofilin, S23,24A (SA), and S23,24E (SE) were incubated with F-actin for 30 min. To serve as a negative control, F-actin was incubated alone (–). F-actin and F-actin–bound cofilin were precipitated via centrifugation, and the amounts of F-actin and cofilin in the supernatant (S) and pellet (P) were analyzed by SDS–PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. Quantitative analysis of amounts of cofilin and F-actin from three independent experiments is shown in the bottom graphs; bars represent SD. Quantification was performed by normalizing the density of bands in the assay to the amount of cofilin or actin in control (*p < 0.05). (B) Microscopic analyses of cofilin-induced F-actin depolymerization and/or severing. Alexa 488– or biotin-labeled actin filaments were incubated with purified MBP or MBP-cofilin wild-type, S23,24A, or S23,24E. Subsequently the filaments were tethered to a glass slide and observed via confocal microscopy. The result of quantitative analyses of the length of actin filaments in three independent experiments is shown in the lower graph (*p < 0.05). The experiments were performed in triplicate, and error bars represent ± SD. (C) Cofilin binding to 14-3-3ζ. Purified MBP-cofilin WT, S3A, S3E, S23,24A, or S23,24E was incubated with FLAG-14-3-3ζ for 60 min. Cofilin-bound 14-3-3ζ was pulled down with an anti-FLAG affinity gel and subjected to SDS–PAGE and Western blotting.