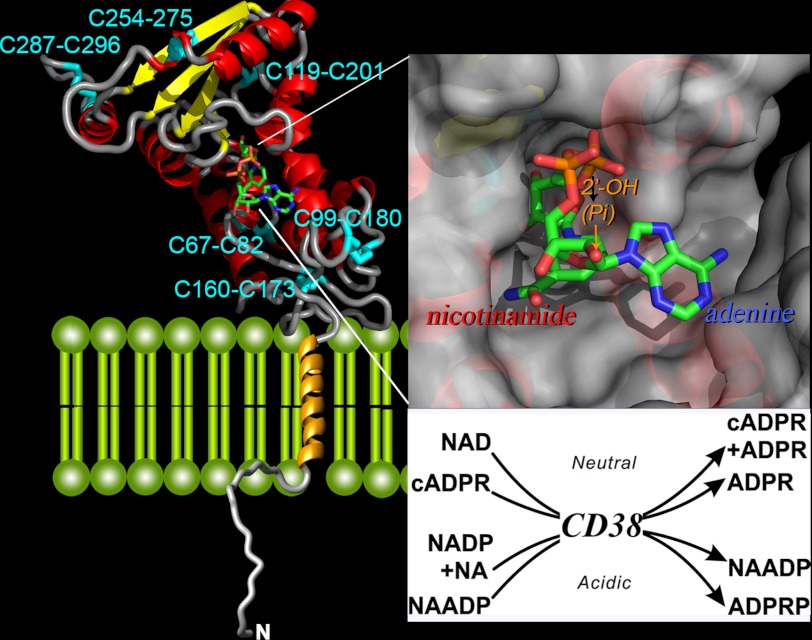
FIGURE 2.
Crystal structure of CD38. The secondary structure of the C-terminal domain of CD38 is shown, with helices in red, β-sheets in yellow, and coils in gray. The disulfides are labeled and colored cyan. The transmembrane segment is modeled as a gold helix, whereas the N-terminal tail as a random coil. A molecule of NAD is bound at the active site near the middle of the C-terminal domain and is rendered in stick configuration. Red, oxygen; orange, phosphorus; green, carbon; blue, nitrogen. The upper inset shows the active site in surface view. The nicotinamide end of the bound NAD enters the site first, whereas the adenine end is positioned toward the opening of the site. The lower inset lists the multiple reactions catalyzed by CD38. The synthesis and hydrolysis of cADPR occur at neutral pH, whereas those of NAADP occur at acidic pH. NA, nicotinic acid, ADPRP, ADP-ribose phosphate.