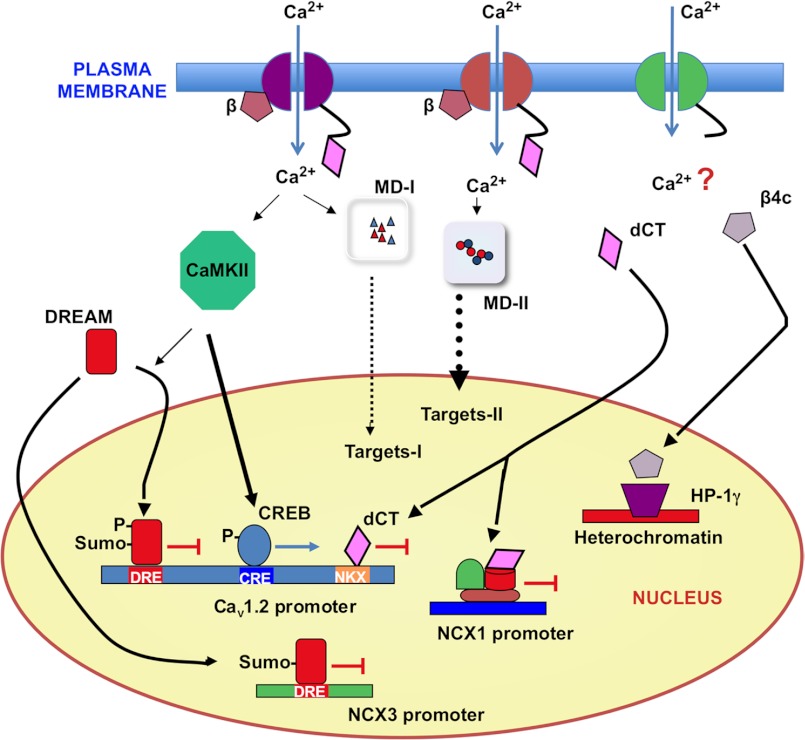
FIGURE 1.
L-type Ca2+ channels and Ca2+-dependent transcriptional regulation. L-type channels regulate their own expression through different Ca2+-dependent transcriptional mechanisms. Differential clustering of L-type channels at the membrane or different subunit composition determines their involvement in distinct microdomains (MD-I or MD-II), different calcium signaling, and final effect on specific sets of target genes. Phospho-CREB-dependent activation through cAMP-responsive element (CRE) sites and repression mediated by sumoylated DREAM through DRE sites and/or the dCT fragment through NKX2.5/MEF/C/EBP and CRM1 sites are also indicated. Additional transcriptional effects of the dCT fragment and the β4c channel subunit through the interaction with several nucleoproteins are shown.