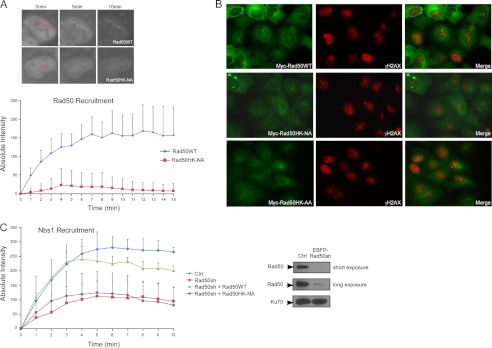
FIGURE 2.
The Rad50 zinc hook domain is important for the recruitment of MRN to chromosomal DSBs. A, recruitment of Rad50 to DNA damage sites in live cells. U2OS cells expressing EGFP-Rad50WT or the hook mutant Rad50HK-NA were induced with DNA DSBs by laser microirradiation. Recruitment of EGFP-Rad50WT and EGFP-Rad50HK-NA to laser-microirradiated sites at indicated time points are shown (upper panel, with red lines showing the laser-induced damage path in precut cells), and the absolute intensities of Rad50 recruitment were determined (bottom panel). B, stable U2OS cell lines expressing Myc-tagged Rad50WT or Rad50 hook mutants Rad50HK-NA and Rad50HK-AA were subjected to laser microirradiation (in which damage path generated by the laser mircrobeam was made as two crossed lines in an X-shaped pattern) and fixed 10 min later, followed by immunostaining using anti-Myc and anti-γH2AX antibodies. C, Nbs1 recruitment in Rad50 hook mutant cells. mRFP-Nbs1 with either EGFP-Rad50WT or EGFP-Rad50HK-NA or vector were co-transfected into U2OS cells, with endogenous Rad50 silenced by shRNAs or mock treated (Ctrl). Rad50 shRNA was engineered into pMKO-EBFP-puro construct, which uses EBFP to indicate cells containing shRNAs. DNA damage was induced by laser microirradiation, and the recruitment intensities of mRFP-Nbs1 were determined. Western blot shows silencing of endogenous Rad50 by EBFP-marked Rad50 shRNAs, with Ku70 used as a loading control.