Figure 1.
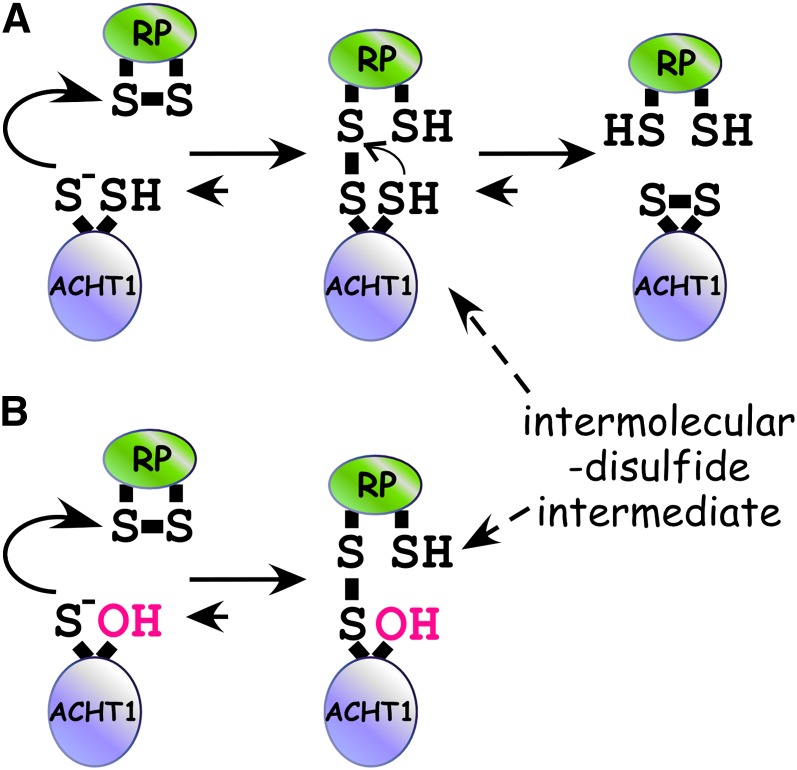
Reaction Scheme of the Two-Step Dithiol Disulfide Transfer Reaction of ACHT1.
(A) Initially, the nucleophilic N-terminal Cys of the ACHT1 active site (s−) attacks the disulfide bond of its redox protein partner (RP), resulting in an intermolecular-disulfide reaction intermediate between ACHT1 and RP. Next, an attack of the C-terminal Cys of the ACHT1 active site on the intermolecular-disulfide bond releases oxidized ACHT1 and reduced RP.
(B) In a redox-active site mutant of ACHT1, in which the C-terminal Cys is replaced with a Ser, the resolving step is inhibited, resulting in increased stabilization of the intermolecular disulfide intermediate.
[See online article for color version of this figure.]