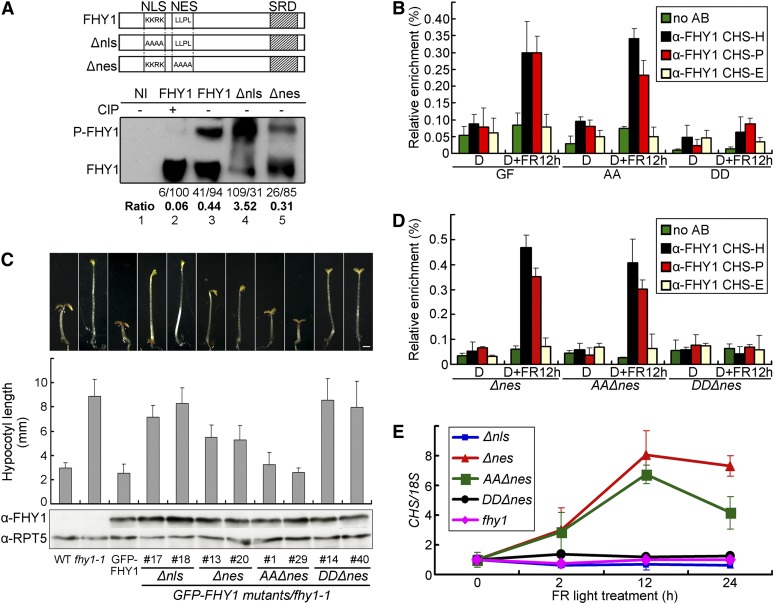
Figure 5.
FHY1 Phosphorylation Prevents Its Association with CHS Promoter.
(A) Phosphorylation of FHY1 occurs in both cytoplasm and nucleus. A diagram of FHY1 constructs showing NLS or NES mutations generated (Top). Tobacco leaves infiltrated with indicated FHY1 constructs were exposed to R for 1 d (Bottom). Protein extracts were treated with (+) or without (−)calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (CIP) before immunoblots with anti-FHY1. The ratios of P-FHY1 over FHY1 are indicated below the immunoblot. Band intensities were normalized to the value (set at 100) of nonphosphorylated FHY1 in lane 2. NI, noninfiltrated tobacco leaves.
(B) P-mimic FHY1 is unable to associate with the CHS promoter. Four-day etiolated seedlings of GFP-FHY1/fhy1-1 (GF), GFP-FHY1S39AT61A/fhy1-1 (AA), and GFP-FHY1S39DT61D/fhy1-1 (DD) were left untreated (D) or treated with 12 h FR (6 µmol/m2/s) (D+FR12 h) and subjected to anti-FHY1 ChIP-qPCR. AB, antibody.
(C) Morphology of FHY1 combined localization and phosphorylation mutants in FR. Two independent transgenic lines for each mutant as indicated (in fhy1-1 background) were grown in FR for 5 d. Measurements of hypocotyl lengths are shown as mean ± sd (n > 20). Immunoblots indicate expression of mutant GFP-FHY1 in corresponding transgenic lines, with RPT5 as a loading control. Bar = 1 mm.
(D) Nuclear P-mimic FHY1 fails to associate with the CHS promoter. GFP-FHY1Δnes/fhy1-1 (Δnes), GFP-FHY1AAΔnes/fhy1-1 (AAΔnes), and GFP-FHY1DDΔnes/fhy1-1 (DDΔnes) seedlings were examined by anti-FHY1 ChIP-qPCR as described in (A).
(E) Nuclear exclusion as well as phosphorylation of FHY1 abolishes CHS activation. Four-day etiolated seedlings of indicated genotypes were irradiated with FR (6 µmol/m2/s). Quantitative RT-PCR of CHS transcript was normalized against that of 18S.
All error bars represent ±sd of triplicate experiments.