Figure 6.
MPK4 Interacts with MEKK2 and Phosphorylates the N Terminus of MEKK2.
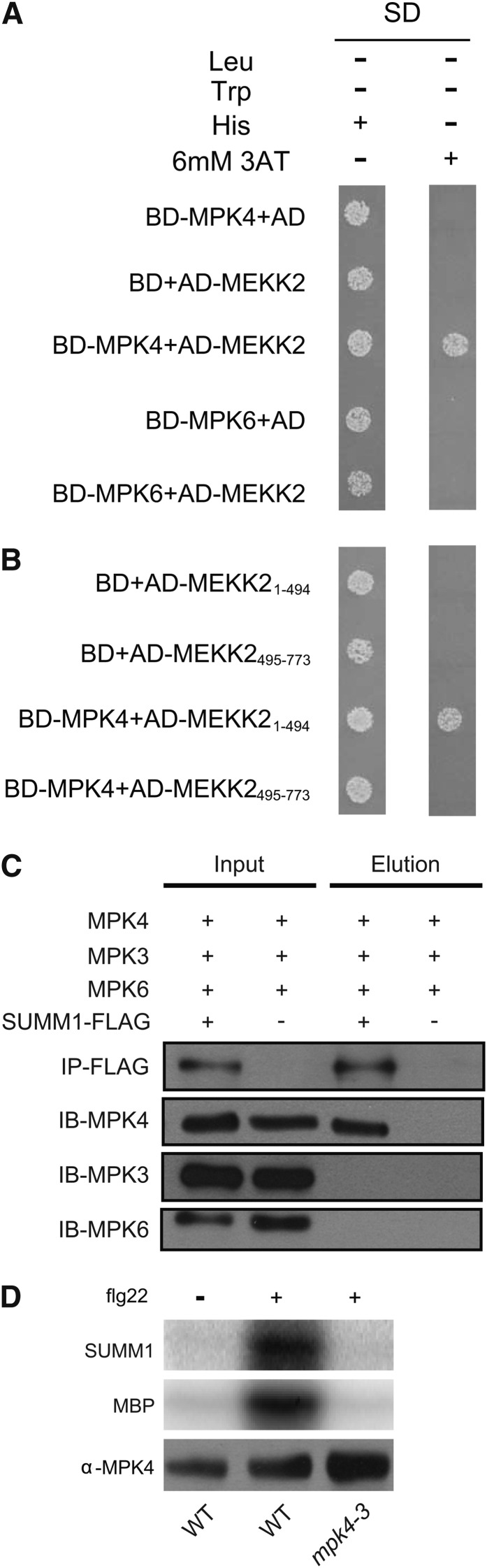
(A) Yeast two-hybrid analysis of the interaction between MPK4 and MEKK2.
(B) Yeast two-hybrid analysis of the interaction between MPK4 and the N-terminal (MEKK21-494) and C-terminal (MEKK2495-773) domains of MEKK2.
(C) Co-IP of MPK4 with MEKK2-3xFLAG in total proteins extracts from SUMM1-3xFLAG transgenic plants. Total protein extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG Sepharose beads. Crude lysates (left panel, Input) and immunoprecipitated proteins (right panels, Elution) were detected with anti-FLAG, anti-MPK4, anti-MPK3, and anti-MPK6 antibodies, respectively. Wild-type plants without the SUMM1-3xFLAG transgene were used as a negative control. This experiment was repeated three times with similar results.
(D) Phosphorylation of the N terminus of SUMM1/MEKK2 by MPK4. MPK4 was immunoprecipitated from the wild type (WT) and mpk4-3. After incubation with [γ-32P]ATP and the immunoprecipitated MPK4 or mpk4-3 mutant protein in protein kinase buffer, the E. coli–expressed N-terminal domain of SUMM1 was separated on 10% SDS-PAGE. The autoradiograph of the gel is shown in the top panel, and immunoblot analysis of MPK4 levels is shown in the bottom panel. This experiment was repeated four times with similar results.