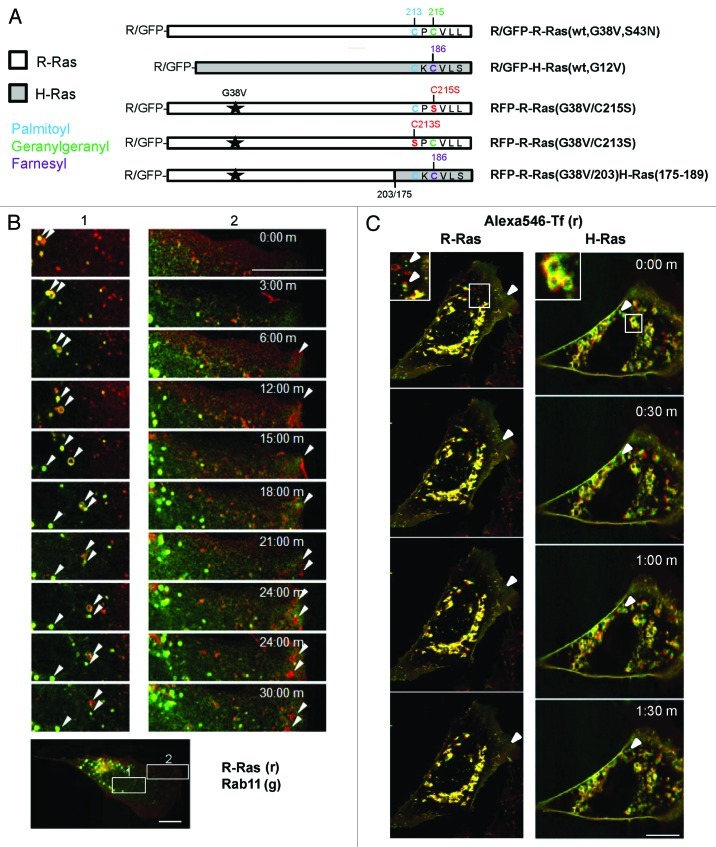
Figure 1. R-Ras traffics to membrane ruffles in recycling vesicles. (A) R-Ras and H-Ras constructs used in this study, expressed as red or green fluorescent protein (RFP or GFP) fusions. G38V and G12V (starred) are constitutively active mutants of R-Ras and H-Ras, respectively. HVR C-terminal sequences are shown with post-translational modification sites indicated: palmitoyl, blue; geranylgeranyl, green; farnesyl, purple; mutations are shown in red. R-Ras(G38V/203)H-Ras(175–189) is activated R-Ras, residues 1–203, deleted in the HVR and replaced with the farnesyl-specific HVR of H-Ras. R-Ras(S43N) is constitutively inactive. (B) R-Ras and Rab11 trafficking in live, spread cells. RFP-R-Ras(G38V) (red) and GFP-Rab11 (green) were tracked in live NIH 3T3 cells by confocal microscopy. Images were acquired every 30 sec to facilitate vesicle tracking; representative images are shown. Left panels (1) show R-Ras anterograde transport with recycling endosomes. R-Ras transport vesicles included Rab11-containing RE and Rab11-negative puncta. Right panels (2) show retrograde R-Ras transport from membrane ruffles that do not contain Rab11. Arrowheads point to individual R-Ras/Rab11 vesicles tracked across images. The lower panel shows a representative image of the whole cell used for imaging, at lower magnification, with zones 1 and 2 indicated by white boxes. (C) R-Ras and H-Ras (wt) partially traffic in transferrin (Tf)-containing RE. Cells expressing GFP-R-Ras or -H-Ras (green) were labeled with Alexa546-Tf (red) by a pulse-chase scheme (see Materials and Methods) and viewed by live confocal microscopy with images acquired every 30 sec. Areas of co-localization are seen as yellow. Inset areas in white boxes are shown at 2x. Arrowheads point to Tf-negative R-Ras or H-Ras vesicles. Bars, 10 μm.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.