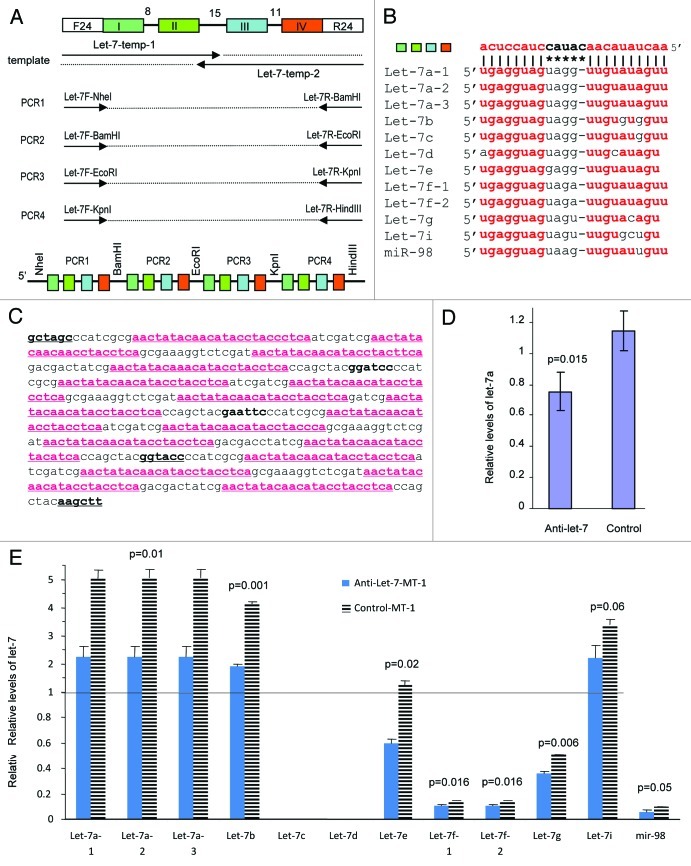
Figure 1. Development of a sponge that can decay levels of let-7 family. (A) Strategy to generate the anti-let-7 construct is shown. It contains 16 motifs that can bind to the different members of the let-7 family. Each PCR product contains four different antisense sequences that can bind to the let-7 family members. It was generated by ligating together four different fragments to have multiple copies of the binding regions. (B) Alignment of one of the anti-let-7 sequences with the 12 members of the let-7 family members. Complete matching of the seed regions with the anti-let-7 sequence and high degrees of matching between the tail regions are shown. (C) Sequence of the anti-let-7 insert. The four different antisense constructs are underlined, which are capable of binding to the 12 members of let-7 family. (D) The efficiency of the anti-let-7 construct in HeLa cells was tested. The construct was able to decrease the levels of the mature miRNAs of the let-7 family members as seen through real-time PCR. Error bars, SD (n = 3). (E) The efficiency of the anti-let-7 construct was tested in MT-1 cells. The construct was able to downregulate mature miRNAs of the let-7 family member from basal levels that was found in the control cells as seen through real-time PCR.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.