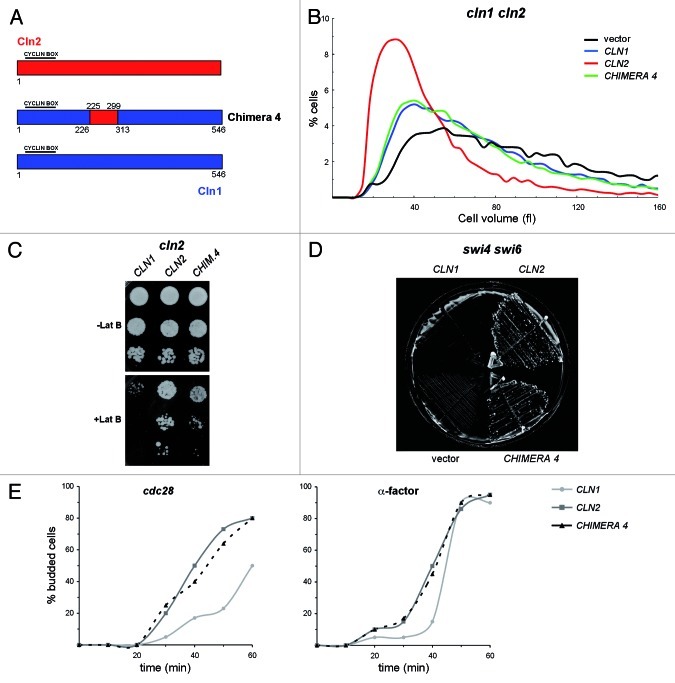
Figure 2. Functional analisys of chimeric cyclin 4. (A) Diagram of chimeric cyclin 4. All cyclins are HA-epitope tagged at the C terminus. Expression is driven by the promoter corresponding to the cyclin at the N-terminal end. (B) Cell size distribution in exponentially growing cultures of the cln1 cln2 mutant strain (JCY847) transformed with an empty vector or a centromeric plasmid containing the CLN1, CLN2 or CHIMERA4 gene. (C) 10-fold serial dilutions from exponentially growing cultures of the cln2 mutant strain (JCY846) transformed with an empty vector or a centromeric plasmid containing the CLN1, CLN2 or CHIMERA4 gene were spotted onto YPD medium and YPD medium supplemented with 25 μM latrunculin B and incubated at 28° for 3 d. (D) Cells of the swi4ts swi6 mutant strain (K2003) transformed with an empty vector or a centromeric plasmid containing the CLN1, CLN2 or CHIMERA4 gene were streaked onto YPD plates and incubated at 37° for 3 d. (E) Exponentially growing cultures of the cdc28ts cln1 cln2 (JCY1048) and the cln1 cln2 (JCY847) mutant strains transformed with a centromeric plasmid containing the CLN1, CLN2 or CHIMERA4 gene were arrested at the G1 phase by incubation at 37° or in the presence of 5 μg/mL α-factor for 3 h, respectively. The budding index was determined at the indicated time after release from cell cycle arrest.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.