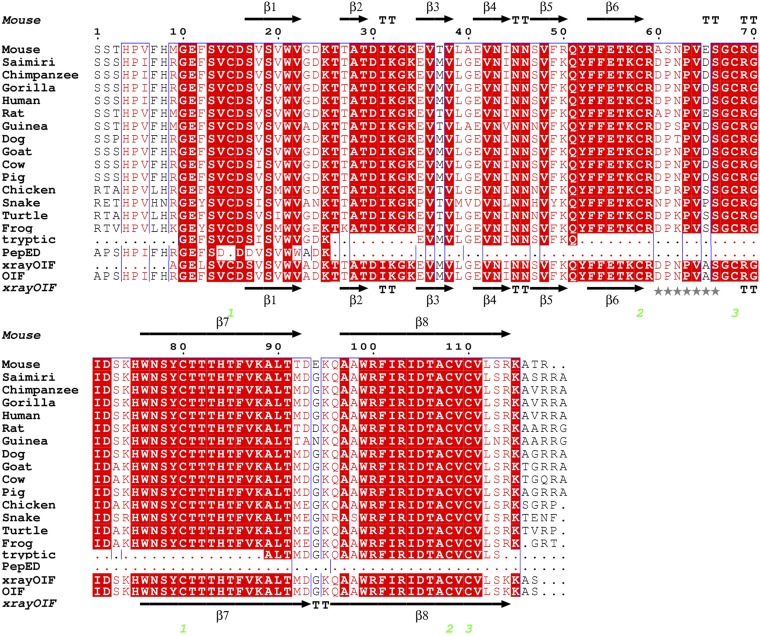
Fig. 2.
Structure-based sequence alignment of ovulation-inducing factor (OIF) from seminal plasma and nerve growth factor (NGF). Sequence alignments of mature OIF (determined by X-ray crystallography sequencing) with NGF from different species (mouse, PDB 1bet; Saimiri boliviensis, Q5ISB0.2; chimpanzee, BAA90438.1; gorilla, Q9N2F0.1; human, PDB 1sg1; rat, P25427.2; guinea pig, P19093.1; dog, AAY16195.1; goat, AFA52664.1; cow, NP_001092832.1; pig, Q29074.1; chicken, P05200.1; snake venom, Q5YF90.1; turtle, ACY72443.1; and frog, P21617.2). Tryptic is the tryptic peptide sequence of llama OIF (residues:10–23, 35–51, 89–99, and 100–113) obtained by LC-MS/MS and PepED is the N-terminal amino acid sequence of llama OIF obtained by internal Edman degradation. Residues are numbered in black and follow the sequence of mouse NGF (PDB 1bet). Solid black arrows indicate β-strands. TT indicates tight turns. Strictly conserved residues are indicated by white letters on a red background. Conservatively substituted residues are indicated by red letters on a white background. The three disulfide bridges between Cys15 and Cys80, Cys58 and C108, and C68 and Cys110 are shown in green numbers. Loops are labeled L1–L4 (blue). Stars indicate flexible loop 3.