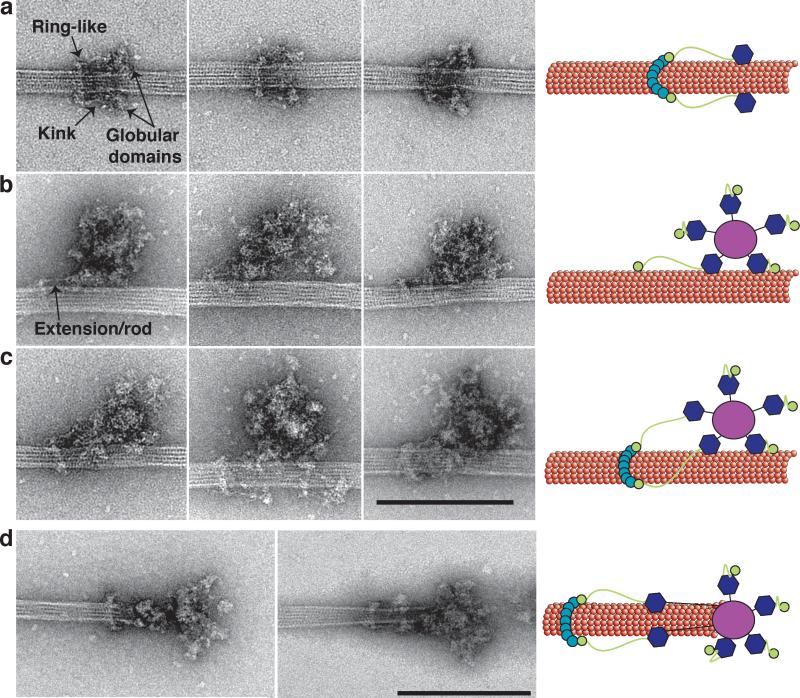
Figure 2. Kinetochore particles bound to taxol-stabilized microtubules.
(a) Representative images of fragments of kinetochore particles (56 nm long) bound to taxol-stabilized microtubules reveal a rod with a kink (arrow) connected to a ring on one end and a globular domain on the opposite end. (b) Large kinetochore particles (126 nm long) bind to microtubules through globular domains and an additional extension/rod (arrow) that emanates from one of the globular domains. (c) Large kinetochore particles bind to microtubules through multiple globular domains and contain an extension that connects to a ring. Scale bar is 200 nm. (d) Two selected images of kinetochores at the tip of taxol-stabilized microtubules. Globular domains extending 50 nm from the central hub bind to the microtubules and are connected to a distal ring 50 nm further. Scale bar is 200 nm. Cartoons on the left schematize the key features of the images.