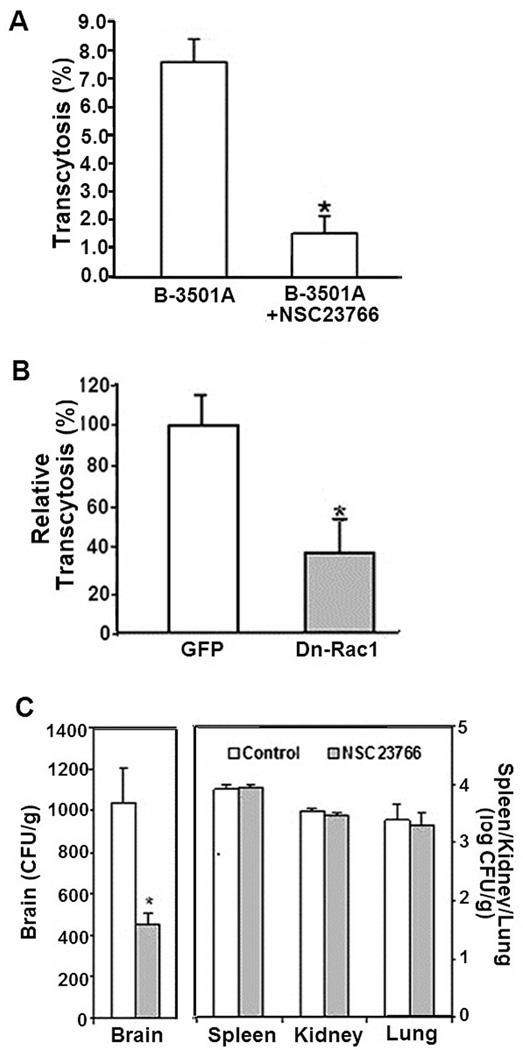
Figure 2. Role of Rac1 in C. neoformans transcytosis across the blood brain barrier.
A. To determine the role of Rac1 in C. neoformans transcytosis, HBMEC monolayers grown on transwells were treated with 100 µM of NSC23766 or vehicle control and incubated with C. neoformans strain B3501A. After 9 hour incubation, transcytosed CFUs were determined as described in Materials and Methods. *p<0.05 compared to vehicle-treated HBMEC
B. HBMEC transfected with adenoviruses expressing dominant-negative Rac1 construct or vector control were examined for transcytosis of C. neoformans strain B3501A and then expressed as relative transcytosis (%) assuming transcytosed yeast numbers in control vector-transfected HBMEC as 100%. *p<0.05 compared to vector-transfected HBMEC
C. To analyze the role of Rac1 in C. neoformans penetration into the brain, mice that received NSC23766 or vehicle control were injected with B-3501A (1×105 cells in 100µl PBS) via the tail vein. 24 hours later, the brains of the mice were removed, homogenized and examined for CFUs by culturing on YPD agar plates. The yeast counts were expressed as CFUs/gm. Kidneys, lungs and spleens were also determined for yeast counts (expressed as CFUs/gm). *p<0.05 compared to PBS-treated animals.