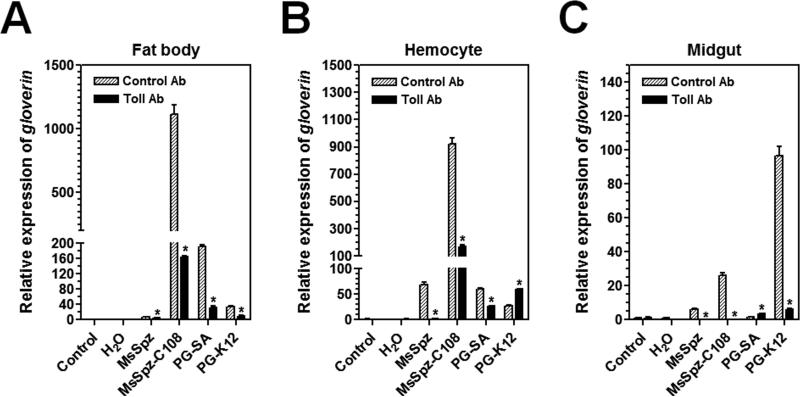
Fig. 5. Activation of Msglv triggered by MsSpz-C108 and bacterial peptidoglycans is blocked by antibody to M. sexta Toll.
Day 1 fifth instar M. sexta naïve larvae were pre-injected with purified IgG to the ecto-domain of M. sexta Toll (Toll Ab, 5 μg/larva) or IgG from pre-immune rabbit serum (Control Ab, 5 μg/larva). One hour later, these larvae were injected with purified recombinant MsSpz (3 μg/larva), MsSpz-C108 (1 μg/larva), S. aureus PG (PG-SA) (1 μg/larva), E. coli PG (PG-K12) (1 μg/larva), or water, or without second injection (control), fat body, hemocytes and midgut were then collected at 20 h after second injection for preparation of total RNAs. Expression of Msglv mRNA was determined by real-time PCR. M. sexta rpS3 gene was used as an internal control. The bars represent the mean of three individual measurements ± SEM. Relative expression of Msglv mRNA after pre-injection of antibody but without second injection (control) was set as 1. Asterisks indicate significant difference (p<0.05) between Toll and Control antibody pre-injections for Msglv determined by an unpaired t-test.