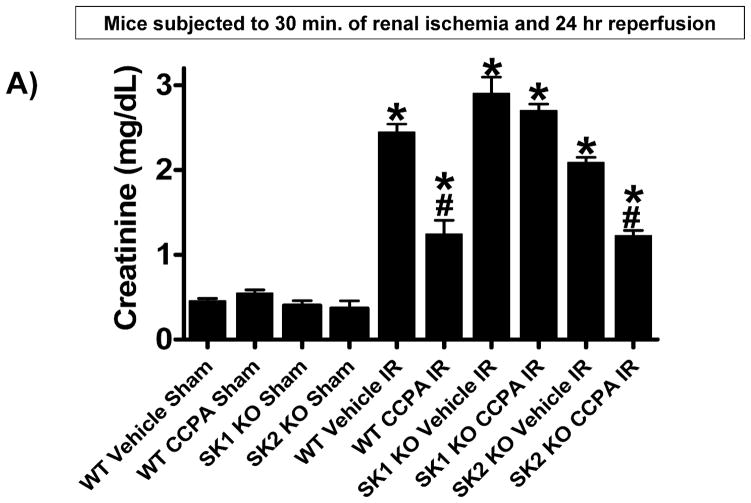
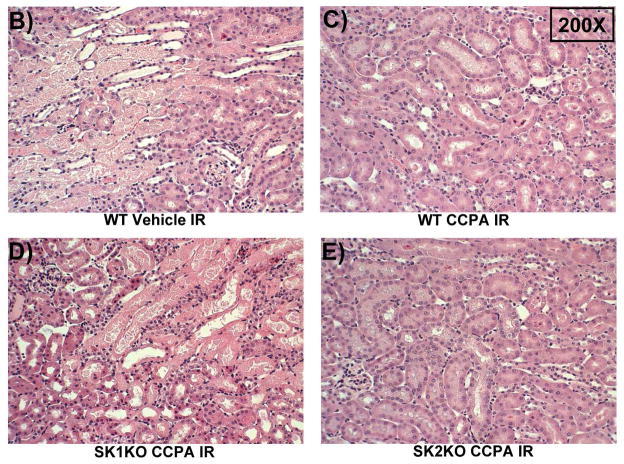
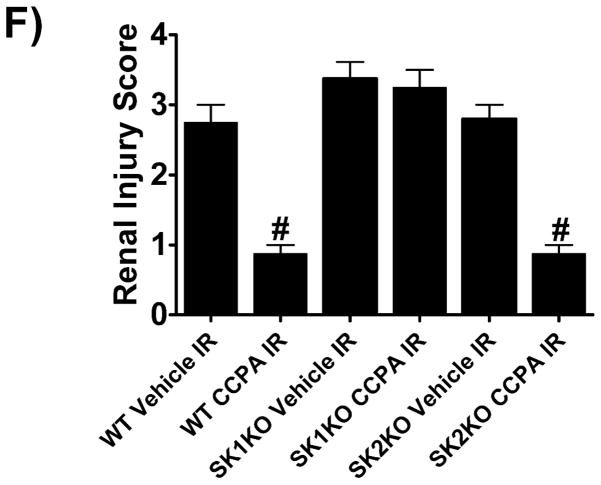
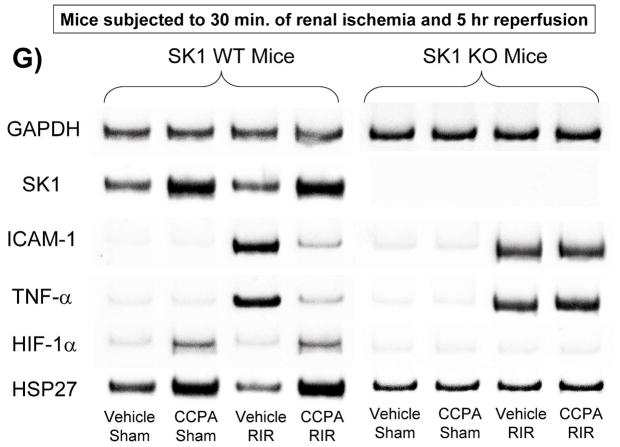
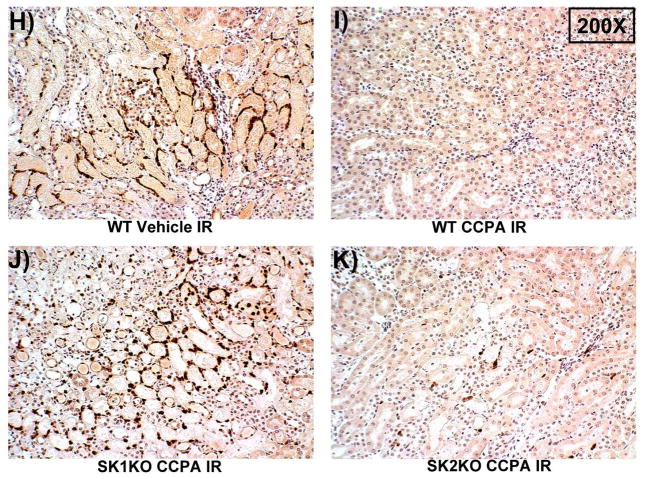
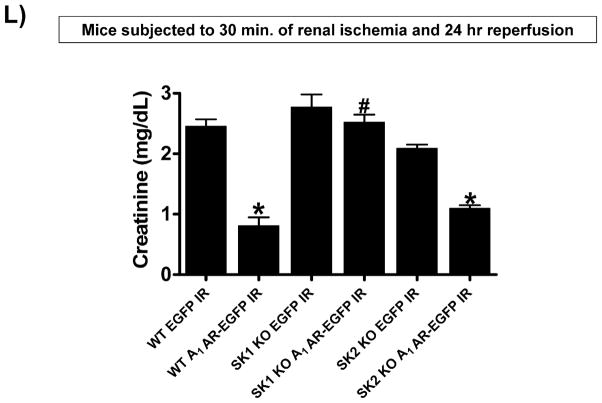
Figure 2. SK1 is critical for A1AR-mediated renal protection against ischemic AKI.
A. Plasma creatinine levels (24 hrs after surgery) from wild type (WT), SK1−/− (SK1 KO) or SK2−/− (SK2 KO) mice subjected to sham-surgery (N=4) or to renal ischemia and reperfusion (IR) after vehicle (0.4% DMSO in saline) or a selective A1AR agonist treatment (CCPA, 0.1 mg/kg, i.p. 15 min before renal ischemia) treatment (N=6 for each group). Treatment with CCPA significantly attenuated the increases in plasma creatinine in WT and SK2−/− mice but not in SK1−/− mice. *P<0.05 vs. vehicle-treated mice subjected to sham-surgery. #P<0.05 vs. vehicle-treated mice subjected to renal IR. B–E. Representative photomicrographs (magnification 200X) hematoxylin and eosin staining of kidney sections of mice subjected to 30 min of renal ischemia followed by 24 hr of reperfusion. Photographs are representative of 4 independent experiments. Vehicle-treated wild-type mice (WT Vehicle IR) showed severe renal tubular necrosis after renal IR (B). CCPA treatment significantly attenuated renal IR injury in WT (C) and SK2−/− mice (E) but not in SK1−/− (D) mice. F. Summary of Jablonski scale renal injury scores (scale 0–4) for mice subjected to sham-operation or renal IR. #P<0.05 vs. vehicle-treated mice subjected to renal IR. Error bars represent 1 SEM. G. Representative RT-PCR bands of TNF-α, ICAM-1, SK1, HIF-1α and HSP27 mRNA in the kidney tissues from SK1+/+ (WT) or SK1−/− (KO) mice (N=4 for each group). Mice were treated with vehicle (0.4% DMSO in saline) or with a selective A1AR agonist (CCPA, 0.1 mg/kg, i.p. 15 min before renal ischemia or sham-operation) and then subjected to sham operation or to 30 min of renal ischemia and 5 hr of reperfusion. Treatment with CCPA induced SK1 and HSP27 mRNA and reduced induction of pro-inflammatory TNF-α and ICAM-1 mRNA expression after renal IR in SK1+/+ mice but not in SK1−/− mice. H-K. Representative immunohistochemistry (magnification 200X) for neutrophil infiltration of kidney sections of mice subjected to 30 min of renal ischemia followed by 24 hr of reperfusion. Photographs are representative of 4 independent experiments. Vehicle-treated wild-type mice (WT Vehicle IR, H) showed many neutrophils after renal IR. CCPA treatment attenuated neutrophil infiltration in WT (I) and SK2−/− mice (K) but not in SK1−/− (J) mice. Secondary antibody conjugated to horseradish peroxidase was developed with diaminobenzidine to stain neutrophils dark brown. L. WT and mice deficient in SK1 or SK2 were renally injected with lentivirus endocing EGFP or A1AR-EGFP 48 hrs prior. WT mice renally injected with A1AR-EGFP lentivirus were protected against renal IR injury (N=4) when compared to EGFP injected WT mice (N=4). In contrast, SK1−/− mice (SK1 KO) renally injected with A1AR-EGFP lentivirus were not protected against renal IR (N=4) when compared to EGFP injected SK1−/− mice (N=4). In contrast, SK2−/− (SK2 KO) mice were protected against renal IR after A1AR-EGFP lentivirus injection (N=4). *P<0.05 vs. EGFP-injected subjected to renal IR. #P<0.05 vs. A1AR-EGFP-injected mice subjected to renal IR