Figure 2. Comparison of structural features between GRP94 and HSP90β.
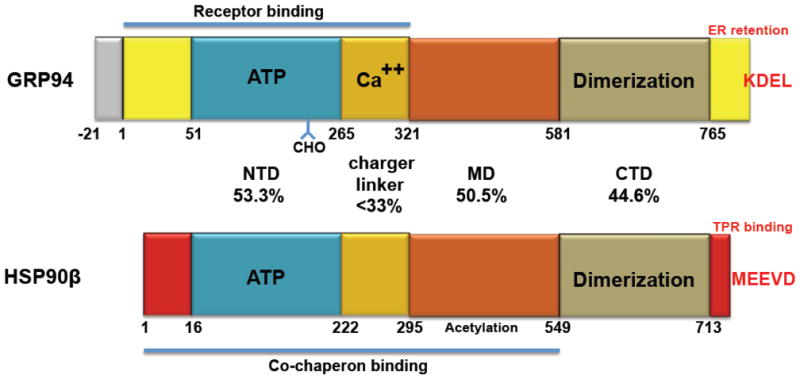
Schematic representation of the domain organization of human GRP94 and human HSP90β. Blue, N-terminal domain (NTD). Beige, charged linker domain. Orange, middle domain (MD). Brown, C-terminal domain (CTD). The similarity between them is indicated by the percent identity indicated for each of the 4 domains. Grey, the signal sequence of GRP94. Yellow and red, unique sequences that distinguish the two members of the family. KDEL, the C-terminal tetrapeptide of GRP94 that serves as the ER retention/retrival ligand for the KDEL receptor [20]. MEEVD, the C-terminal peptide of HSP90, which serves as the target for binding of various TPR containing proteins. ATP, the nucleotide binding site. CHO, the N-glycosylation site of GRP94. Ca++, the known calcium binding activity of the charged linker of GRP94 [92].
