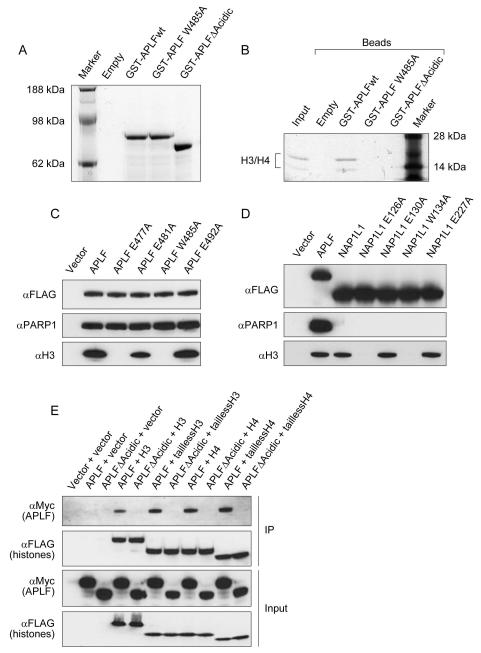
Figure 2. Mode of H3/H4 recognition by APLF resembles NAP1 family of histone chaperones.
A, Coomassie-stained gel showing purified GST-tagged APLF proteins. B, Binding of purified H3/H4 tetramer by GST-tagged APLF variants in vitro. C, Mutation of specific residues within the NAP1L-motif of APLF reduces its interaction with H3/H4 in vivo. D, Mutation of specific residues within the NAP1L-motif of human NAP1L1 abolishes its interaction with H3/H4 in vivo. E, APLF binds to the globular region of H3 and H4 through its acidic C-terminus. In figures 2C, 2D and 2E, the in vivo complexes were purified by immunoprecipitation of transiently expressed FLAG-tagged proteins in HEK293T cells and analyzed by Western-blotting.