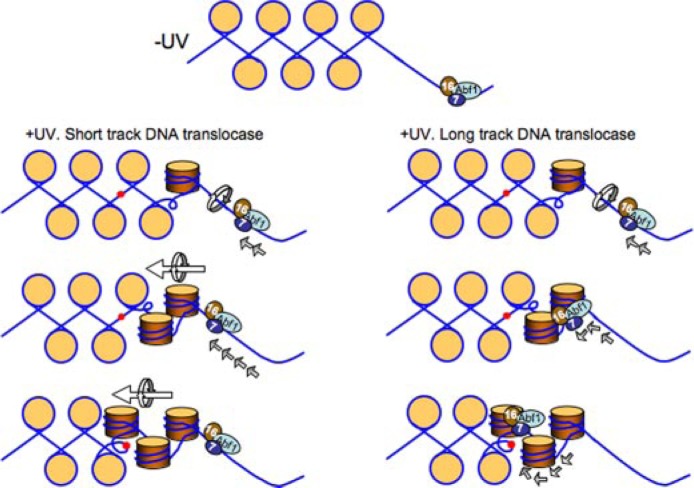
FIGURE 8.
Proposed model of GG-NER complex function at the HMLα locus ABF1-binding site. In the absence of UV radiation the GG-NER complex binds in a specific orientation to the ABF1-binding site (top panel). Following UV radiation the directional DNA translocase activity of the complex results in changes in occupancy of the GG-NER complex at the ABF1-binding site. This generates a domain of altered superhelical torsion in one direction from the ABF1-binding site. This action promotes efficient GG-NER within the domain. The GG-NER complex could generate superhelical torsion by DNA translocation over a short distance from the ABF1-binding site, for example tens of base pairs generating a domain of torsion over hundreds of base pairs (left panel), or by long distance tracking of the complex throughout the domain (right panel). Note that the translational setting of the nucleosomes (beige circles) on the DNA is not perturbed by this process. DNA damage is represented by red spots. 7, Rad7; 16, Rad16.