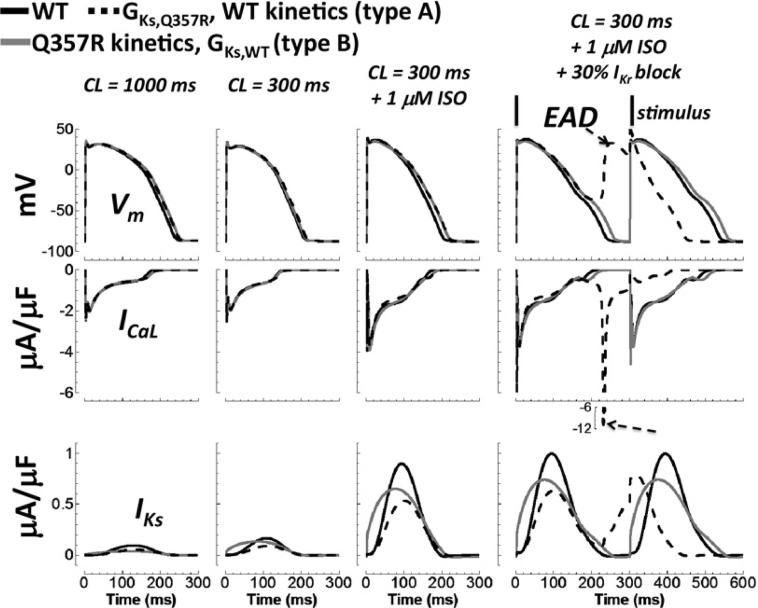
Figure 5.
Effect of reduced conductance versus kinetic changes in the silent mutation. WT, WT with Q357R conductance (mutant type A), and WT with Q357R kinetics (mutant type B) are black, dashed black, and gray lines, respectively. Descending rows show the AP, ICaL, and IKs. The four columns, from left to right, show the cases for normal pacing under basal conditions, fast pacing under basal conditions, fast pacing with application of ISO, and 30% IKr block in addition to fast pacing and ISO. Insults of fast pacing with ISO caused AP prolongation relative to WT. With addition of IKr reduction, kinetic changes alone did not cause EAD formation, but reduced conductance alone did (arrows, rightmost column). AP = action potential; CL = cycle length; EAD = early afterdepolarization; ISO = isoproterenol; WT = wild type.