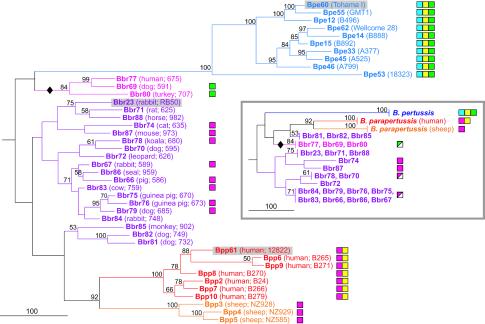
FIG. 2.
Phylogeny of Bordetella strains based on CGH data. Phylogenetic associations were inferred using a maximum-parsimony algorithm, and confidence intervals were determined from 100 bootstrapped datasets. The scale bar represents 100 evolutionary events (steps), and bootstrap values of ≥50% are indicated (19). The presence of Bordetella IS elements, as detected by CGH, is indicated for each strain: blue boxes, IS481; yellow, IS1002; and green, IS1663. The presence of IS1001 (magenta), which was not represented on the array, is taken from reference 46. In that study, the presence of IS1001 was not determined for B. pertussis, excepting strains Tohama I and 18323. In parentheses following each strain number are the strain's host and alias. Sequenced strains are shaded. The diamond indicates the B. bronchiseptica clade that may be associated with B. pertussis. The inset shows an overview tree of an equally likely phylogeny, created by collapsing all branches supported by bootstrap values of ≥50.