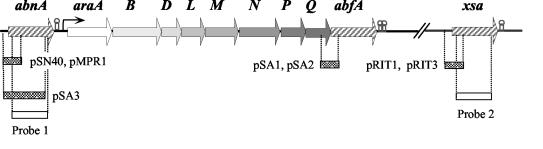
FIG. 1.
Localization of the abnA, abfA, and xsa genes on the B. subtilis chromosome. The three genes are represented by striped arrows pointing in the direction of transcription. abfA belongs to the araABDLMNPQ-abfA metabolic operon, abnA is located immediately upstream, and the xsa gene is positioned 23 kb downstream of the metabolic operon. Hairpin structures indicate potential terminators. The dotted boxes below the physical map represent the extension of the inserts fused to the lacZ gene in the indicated plasmids, and the open boxes represent the fragments used as probes for Northern analysis of the abnA (probe 1) and xsa (probe 2) transcripts. Plasmids pMPR1, pSA1, and pRIT3 were integrated into the host chromosome by means of a single-crossover (Campbell-type) recombinational event that occurred in the region of homology of the resulting strains (Table 1). Linearized DNA from plasmids pSN40, pSA3, pSA2, and pRIT1 was used to transform B. subtilis strains (Table 1), and the fusions were integrated into the chromosome via double recombination with the back and front sequences of the amyE gene.