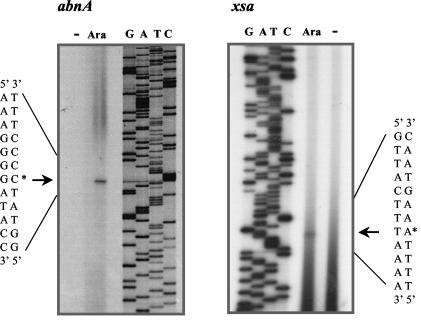
FIG. 4.
Mapping of the transcriptional start site of the abnA and xsa genes. Radiolabeled oligonucleotides ARA86 and ARA90 (Table 2), complementary to the abnA and xsa sequences, respectively, were hybridized and used to direct cDNA synthesis from total B. subtilis 168T+ RNA isolated from exponentially growing cells in the absence (−) or presence (Ara) of arabinose (see Materials and Methods). After extension, the products were analyzed by gel electrophoresis together with a set of dideoxynucleotide chain termination sequencing reactions by using the same primers and plasmids pMPR2 and pRIT3, respectively, as templates. Arrows and asterisks indicate the positions of the abnA- and xsa-specific primer extension products and the deduced start site of transcription, a G residue in the abnA sequence (left) and a T residue in the xsa sequence (right).