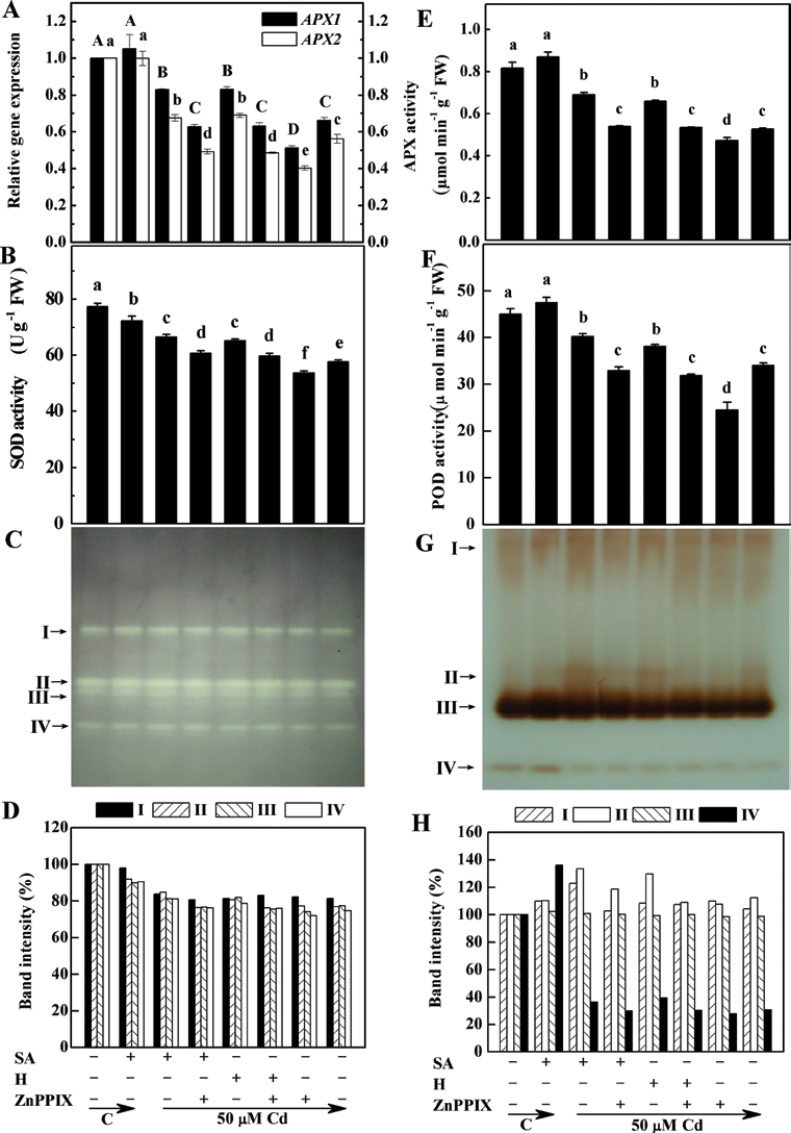
Fig. 4.
Effects of salicylic acid (SA), ZnPPIX, and haemin (H) pre-treatment on the expression and activities of ascorbate peroxidase (APX), and total and isozyme activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and guaiacol peroxidase (POD) in the root tissues of alfalfa upon Cd stress. Five-day-old seedlings were pre-treated or not with 10 µM SA, 20 µM haemin (H), 100 µM ZnPPIX alone, or the combination treatments for 12h, and then exposed to 50 µM CdCl2 for another 24h. The sample without chemicals was the control (C). Then, the APX1/2 transcript quantification test was carried out, normalized against expression of two internal reference genes in each sample (A). SOD (B), APX (E), and POD (F) activity was also determined. Values are means ±SE of three independent experiments with at least three replicates for each. Bars with different letters are significantly different at P < 0.05 according to Duncan’s multiple range test. For the determination of the in-gel activity of SOD (C) and POD isozymes (G), extracts of root apices containing 100 µg of protein were loaded onto native gradient PAGE (5–20%) and, following electrophoresis, the gels were stained. Relative activities of different SOD and POD isozymes are also shown in (D) and (H), respectively. Band intensities of the individual isozymes are expressed as a percentage of the control values. The arrows indicate the bands corresponding to various isozymes.