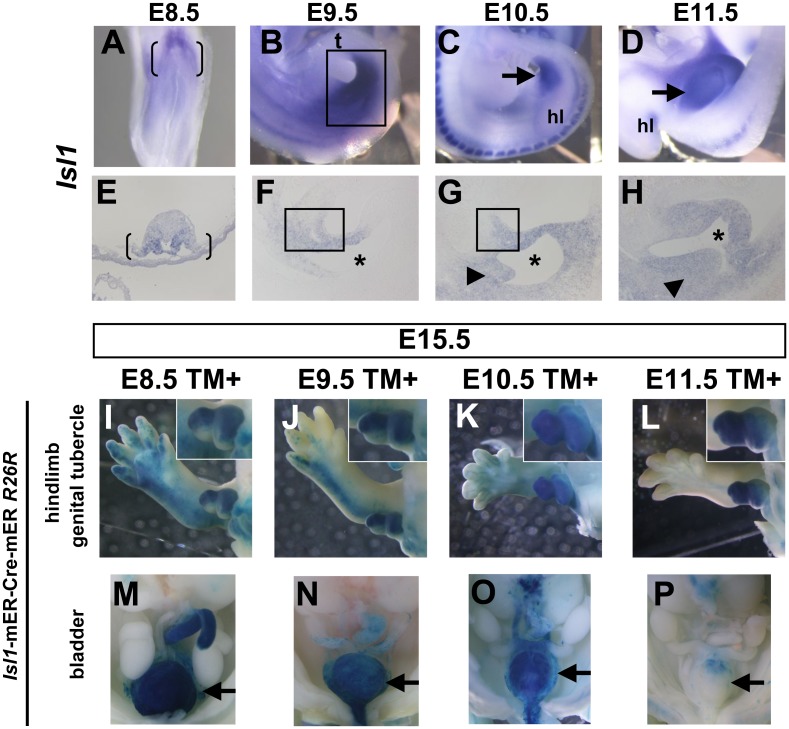
Figure 3. Tissue contribution of Isl1-expressing cells to the caudal body.
(A–H) Expression pattern of Isl1 mRNA during caudal body development. (A, E) Isl1 is expressed in the lateral plate mesoderm adjacent to the future hindlimb bud and the base of the allantois at E8.5 (bracket in A and E). (B, F) Isl1 is expressed in the caudal body region and hindlimb bud at E9.5 (square in B). Its expression is detected in the peri-cloacal regions (square in F). (C, G) Isl1 expression is detected in the cloacal region at E10.5 (arrow in C). It is expressed in the URS (arrowhead in G) and cloacal mesenchyme including aPCM (square in G). Isl1 expression in the hindlimb bud is reduced at E10.5. (D, H) Its expression is maintained in the developing GT at E11.5 (arrow in D). Its expression is detected in GT mesenchyme and URS (arrowhead in H). Asterisk indicates cloaca. (I–P) The R26R-lacZ Cre reporter shows LacZ staining of caudal body regions in Isl1-mER-Cre-mER embryos at E15.5 after administration of tamoxifen at E8.5–E11.5. Whole-mount view of stained embryos of hindlimb and external genitalia (I–L) and pelvic organs (M–P). Isl1-expressing cells contribute to the hindlimb, external genitalia and bladder. Insets in I–L are high magnification of GT. Ventral GT is located at the bottom. t, tail; hl, hindlimb bud.