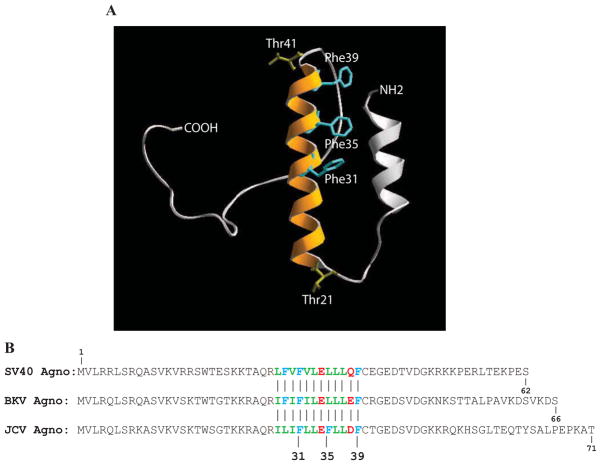
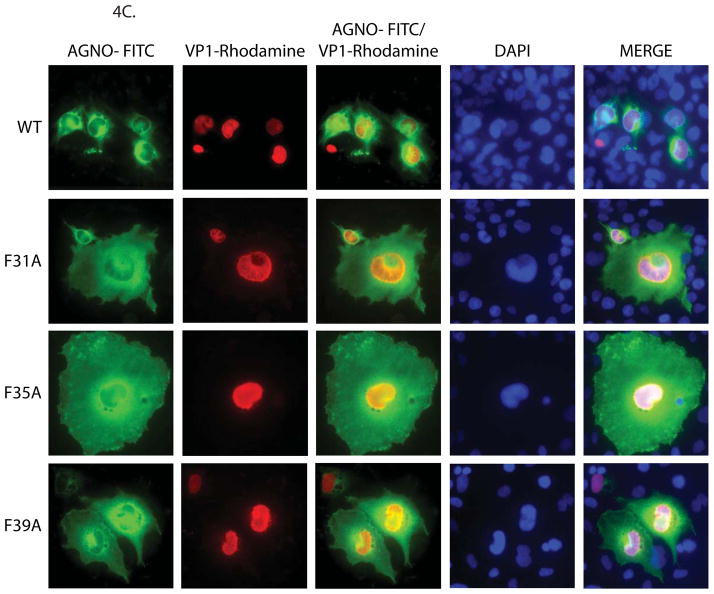
Figure 4.
Structural model of agnoprotein and immunocytochemical analysis of F31A, F35A and F39A mutants. (A) Three-D model of JCV agnoprotein was predicted using I-Tasser program (Roy, Kucukural, and Zhang, 2010). Positions of the three Phe residues are indicated on the α-helical structure. (B) Alignment of SV40, BKV and JCV agnoprotein sequences. (C) Immunocytochemical analysis of F31A, F35A and F39A mutants of agnoprotein in the infected cells. SVG-A cells were transfected/infected either with JCV Mad-1 WT or JCV Mad-1 Agno-F31A or JCV Mad-1 Agno-F35A or JCV Mad-1 Agno-F39A mutant genome and at day 5, cells were fixed with cold acetone and blocked with 5% BSA prepared in PBST for 2h. Cells were then incubated with a combination of α-Agno (rabbit polyclonal, 1:200 dilution) (Del Valle et al., 2002) and α-VP1 (PAB597, mouse monoclonal, 1:200 dilution) (Saribas et al., 2011) overnight. Cells were first washed with PBST three times with (10 min intervals) and incubated with the combination of FITC-conjugated anti-rabbit goat and Rhodamine-conjugated anti-mouse goat secondary antibodies for 45 min. Cells were finally washed with PBST three times with 10 min intervals, mounted with mounting media and examined under a fluorescence microscope.