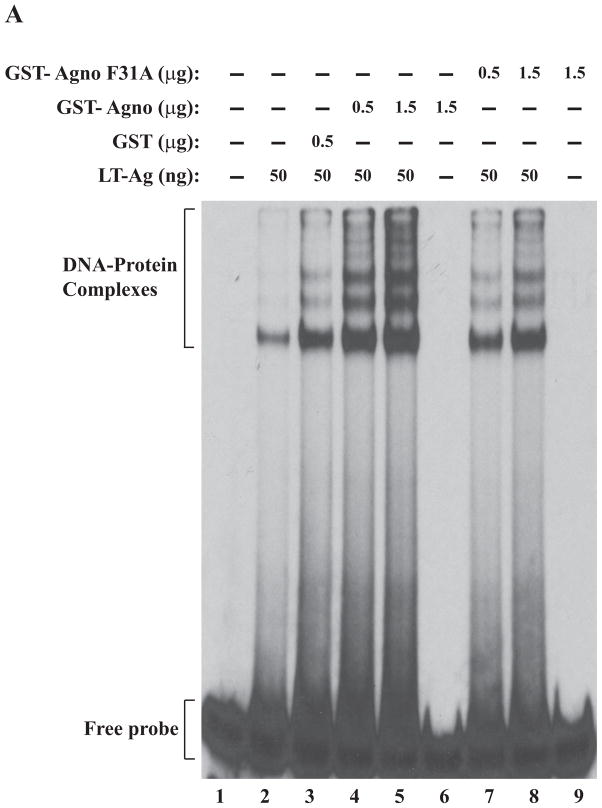
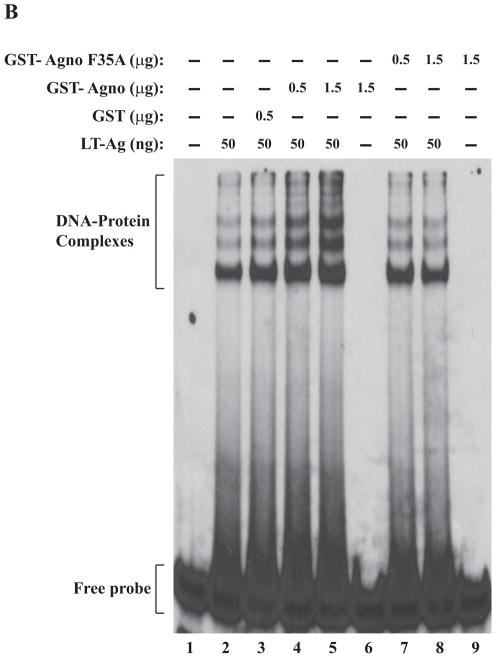
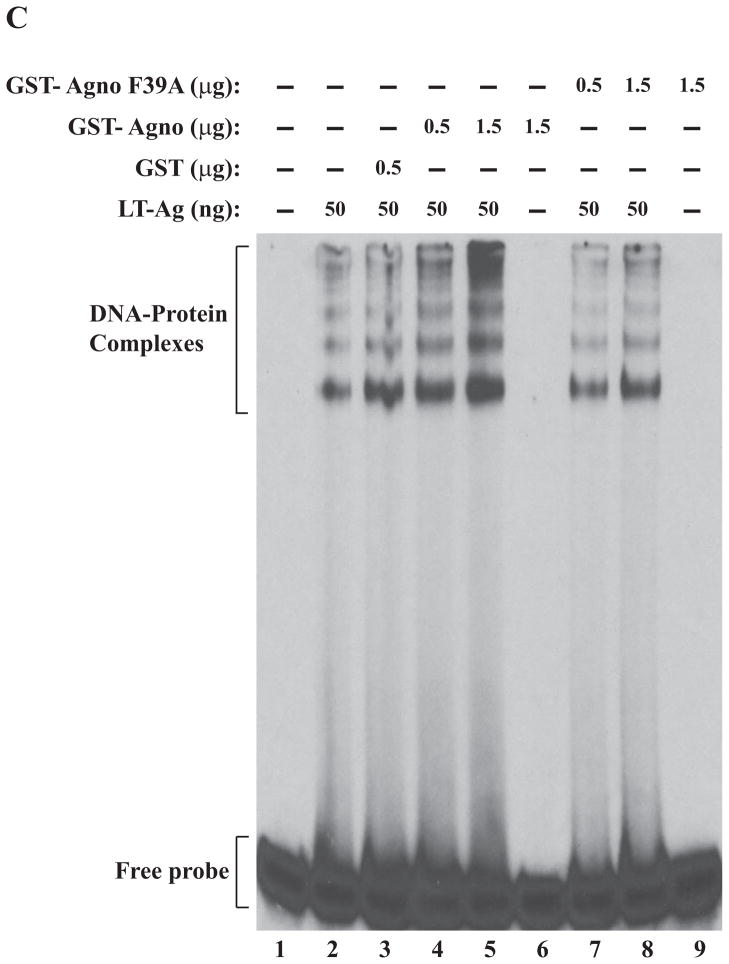
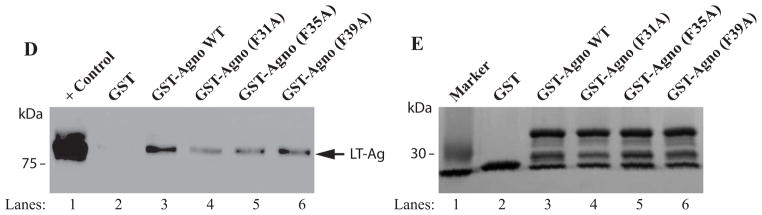
Figure 5.
F31A, F35A and F39A mutants of agnoprotein failed to enhance LT-Ag binding to Ori. (A, B and C) F31, F35 and F39 were substituted with Ala by Quik-Change™ mutagenesis kit and mutant DNA was subcloned into pGEX1λT vector at BamHI/EcoRI sites. Subsequently, the mutant proteins were produced in E. coli and purified as described in Materials and Methods and used in band shift assays as indicated. The band shift assay conditions were identical to those described under the legend for figure 2A. In lane 1, probe alone was loaded on the gel. (D) Analysis of the interaction of agnoprotein point mutants [GST-Agno (F31A), GST-Agno (F35A) and GST-Agno (F39A)] with JCV LT-Ag by a GST pull-down assay. Whole-cell extracts prepared from HJC-15b cells, which express JCV LT-Ag constitutively (Raj, 1995), were incubated with either GST alone or GST-Agnoprotein WT or agnoprotein point mutants fused to GST [GST-Agno (F31A), GST-Agno (F35A) and GST-Agno (F39A)] as described in Materials and Methods. Beads were washed extensively and proteins interacting with GST or GST-Agno Phe mutants [GST-Agno (F31A), GST-Agno (F35A) and GST-Agno (F39A)] were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-LT-Ag antibody (Ab-2). In lane 1, 15 μg of whole-cell extract were loaded as a positive (+) control. (E) Analysis of the GST and GST-Agno WT and agnoprotein point mutants [GST-Agno (F31A), GST-Agno (F35A) and GST-Agno (F39A)] by a 10%-SDS-PAGE followed by coomassie staining.