Figure 8.
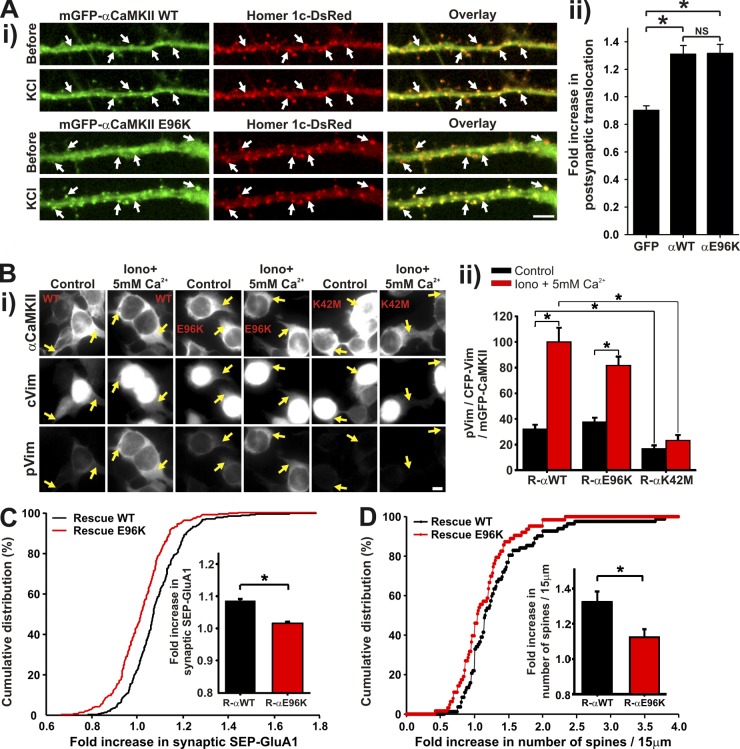
E96K, an active mutant of αCaMKII that translocates to synapses, but not to microtubules, impairs activity-dependent increase in surface GluA1 synaptic insertion and spine remodeling. (Ai) Neurons transfected with mGFP-αCaMKII WT or E96K and Homer1c-DsRed and stimulated with KCl for 1 min. (ii) Fold increase in CaMKII postsynaptic translocation, cotransfected or not with Homer1c-DsRed during the KCl stimulation. Because CaMKII postsynaptic translocation was not different with or without Homer1c coexpression, all neurons were pooled together (n = 13–22 neurons per condition, 6 experiments). (Bi) HEK cells cotransfected with mGFP-αCaMKII WT, E96K or K42M, and CFP-cVim. The cells were stimulated (HBSS + 10 µM ionomycin + 5 mM Ca2+) or not (HBSS) for 5 min, fixed, and immunolabeled for phospho-Vim. (Bii) Quantification of cVim phosphorylation by αCaMKII WT, E96K, and K42M. The intensity of pVim immunolabeled was divided by the intensity of both total cVim and CaMKII. n = 351–536 cells per condition, 2 experiments. Bars, 5 µm. (A and B) *, P < 0.05 Kruskal-Wallis followed by Tukey’s least-significant difference test. (C) Histogram and cumulative distribution of the fold increase in SEP-GluA1 for synapses of neurons with synaptic translocation (S+) of mCherry-αCaMKII WT or E96K rescue, in the presence of shRNA against αCaMKII, during a stimulation with 0Mg2+/Gly for 5 min. (n = 8 neurons, 272–300 synapses per group). (D) Histogram and cumulative distribution of the fold increase in the number of spines on 15-µm dendritic sections in neurons expressing mGFP-αCaMKII WT or E96K rescue as well as mCherry and shRNA against αCaMKII. (n = 6–8 neurons, 63–82 dendritic sections). (C and D) *, P < 0.05 two-sided rank sum test.