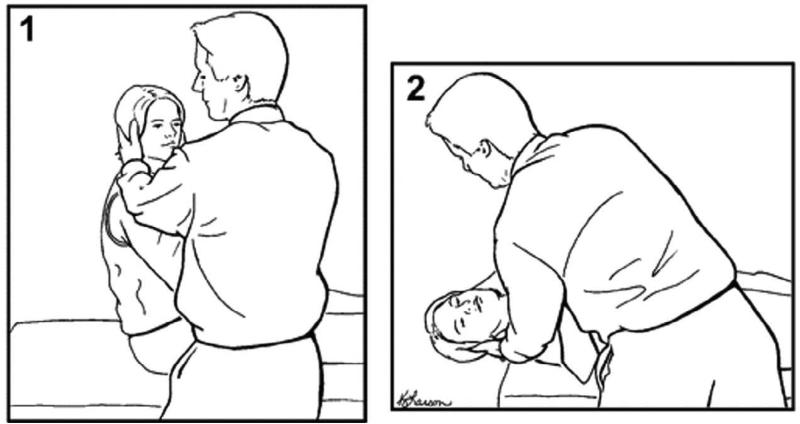
Figure 1.
The Dix-Hallpike test for the diagnosis of posterior canal BPPV [COMP, USE FULL PAGE WIDTH OR NEARLY FULL PAGE WIDTH FOR FIGURE 1]
The patient begins by sitting up right with head is turned 45 degrees toward the side to be tested (1). The patient is then laid back to supine position with head still turned and slightly extended (2). In a positive test torsional nystagmus with the upper pole of the eyes beating toward the dependent ear appears within a few seconds and disappears in less than a minute. A positive Dix-Hallpike test indicates the presence of posterior canal BPPV in the dependent ear. (Adapted from Fife et al. 2008 (25), used with permission)