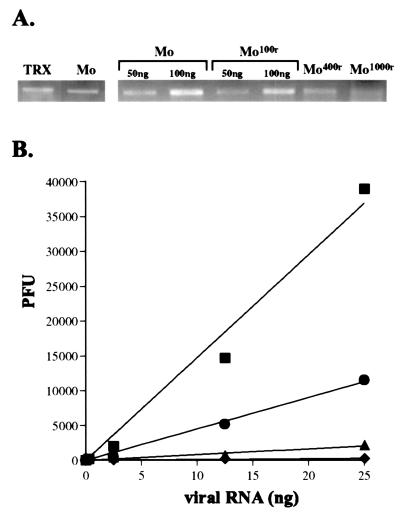
Figure 2.
Direct antiviral effect of ribavirin on the viral genetic material. (A) Total poliovirus genomic RNA accumulation in infected cells, with and without ribavirin. On the Left, normal poliovirus genomic RNA (Mo) isolated from infected cells is normalized to a known quantity (100 ng) of in vitro-generated poliovirus genomes (TRX). On the Right, quantities of poliovirus genomic RNA isolated from infected cells in 100 μM ribavirin (Mo100r), 400 μM ribavirin (Mo400r), and 1,000 μM ribavirin (Mo1000r), are normalized to amounts of poliovirus genomic RNA from infected untreated cells (Mo). Comparisons are tabulated in Table 2. (B) Large reductions in specific infectivity of ribavirin mutagenized RNA virus genomes. Genomic poliovirus RNA from (■) untreated cells, (●) 100 μM ribavirin-treated cells, (▴) 400 μM ribavirin-treated cells, and (♦) 1,000 μM ribavirin-treated cells was tested for specific infectivity in a series of infectious center assays. Data are shown with a linear curve fit for each series. Assays were performed multiple times; data from a representative experiment is shown.