Fig. 2.
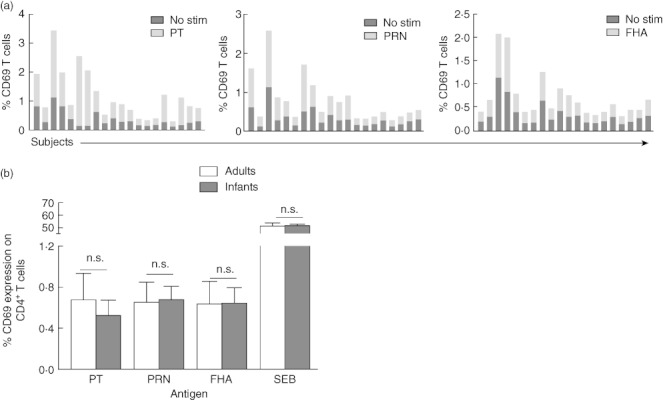
CD69 expression levels on CD4+ T cells after antigen stimulations. After stimulation with each antigen [pertussis toxoid (PT), pertactin (PRN) and filamentous haemagglutinin (FHA)], percentages of CD69 expressing CD4+ T cells among 20 infants were enumerated and plotted against respective unstimulated controls (a). The overall CD69 expression was also compared between infants and adults groups. Shown are percentages of CD4+ T cells expressing CD69 (mean ± standard error of the mean) in response to various diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis (DTaP) antigens and Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) as a positive control in infants and adults (b).
