Figure 1.
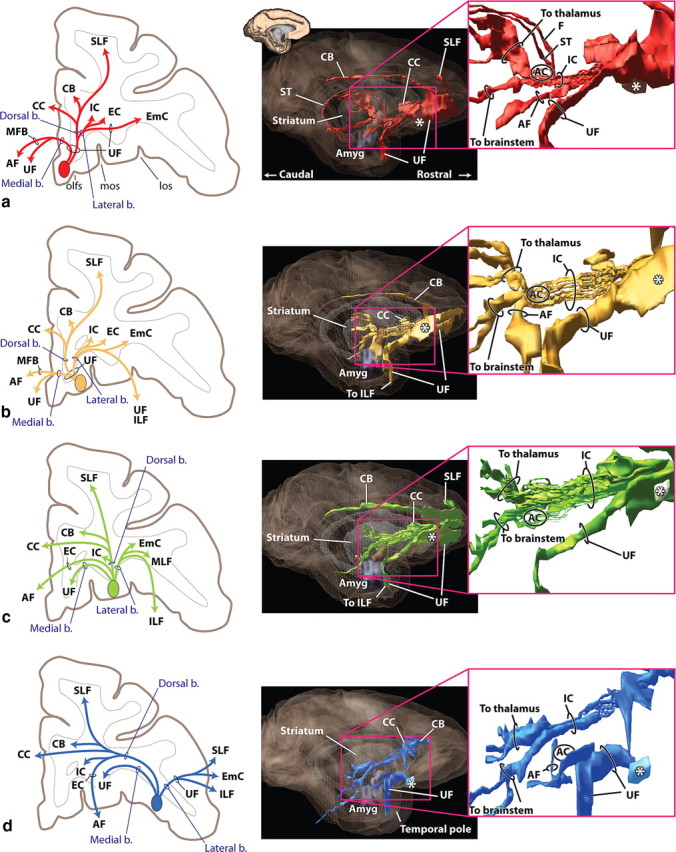
vPFC fiber pathways. a, vmPFC. b, mOFC. c, cOFC. d, lOFC. Left panels illustrate how different bundles separate from the injection site as they enter the white matter. Note, in each case, fibers divide into medial, dorsal, and lateral pathways (blue). However, the specific bundles that are carried within each depend on the position of the origin of the fibers. Right panels illustrate 3D renderings of a lateral view of a sagittal plane. Each is accompanied with an inset to better visualize the separation of fiber bundles. External and extreme capsule pathways have been removed for clarity. Asterisks indicate the rostrocaudal position of the injection site. AC indicates location of the anterior commissure. Axons from the vPFC, mOFC, and cOFC travel ventral or through the AC. Note that axons traveling through the internal capsule divide into dorsal thalamic fibers and ventral brainstem axons. Pathways traveling to the temporal lobe (uncinate fasciculus and ventral amygdalofugal bundle) primarily arise from separate bundles. AF, Ventral amygdalofugal pathway; Amyg, amygdala; b., bundle; CB, cingulum bundle; CC, corpus callosum; EC, external capsule; EmC, extreme capsule; F, fornix; IC, internal capsule; ILF, inferior longitudinal fasciculus; los, lateral orbital sulcus; MFB, medial forebrain bundle; MLF, middle longitudinal fasciculus; mos, medial orbital sulcus; olfs, olfactory sulcus; SLF, superior longitudinal fasciculus; ST, stria terminalis; UF, uncinate fasciculus; *injection site location.
