Figure 3.
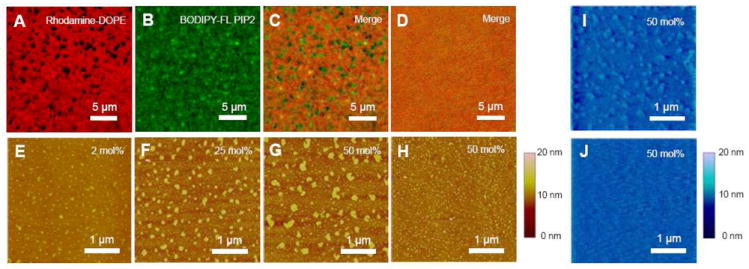
Ca2+ induces phase separation of L-α-PIP2 in background SOPC on supported lipid monolayers. Fluorescence images of 50 mol% PIP2 dual labeled with (A) 0.1 mol% Rhodamine-DOPE and (B) 0.1 mol% C16 BODIPY-FL PI(4,5)P2, were merged in (C), showing Ca2+-induced phase demixing. (D) The phase demixing is reversed by adding excess EDTA. Without fluorescent lipids, Ca2+-induced phase demixing is shown by tapping mode AFM with (E) 2 mol%, (F) 25 mol%, and (G) 50 mol% PIP2. (H) Under the same PIP2 fraction and cation concentration, Mg2+-induced PIP2 clusters are much smaller. The transferred lipid monolayers immersed in buffer (I) with and (J) without Ca2+ are examined also by fluid-phase contact mode AFM. Divalent cation concentration is 1 mM through (A) to (I), while 10 mM EDTA is also added in (D) to test reversibility. Supported lipid monolayers are transferred at constant surface pressure (20 mN/m) unless otherwise indicated.
