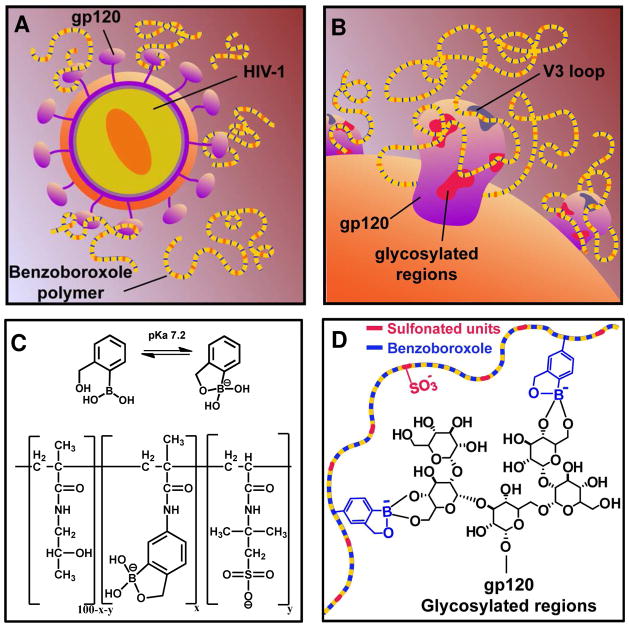
Figure 1.
(A) Graphical depiction of the multivalent benzoboroxole-functionalized polymer interacting with the gp120 complex of HIV-1. (B) Schematic illustration of the binding between the polymers (shown in panel C) and the gp120 through interactions between benzoboroxole groups and the gp120 and/or through interactions between the anionic polysulfonate polymer and the cationic peptide fragments in the V3 loop of the gp120. (C) Chemical structure of benzoboroxole and the linear water-soluble polymers containing benzoboroxole and 2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic synthesized using a HPMA polymer backbone. (D) Hypothetical scheme of the binding chemistry between the multivalent polymers and the glycosylated regions on the gp120 heterotrimer.