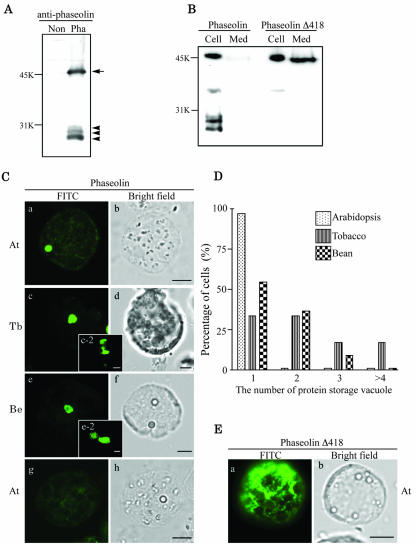
Figure 1.
Expression and localization of phaseolin in leaf protoplasts of three plant species. A, Western-blot analysis of phaseolin in Arabidopsis. Protein extracts were prepared from protoplasts transformed with phaseolin (Pha) and untransformed protoplasts (Non) 24 h after transformation and were analyzed by western-blot analysis using an antiphaseolin antibody. Arrow and arrowheads indicate unprocessed and processed forms of phaseolin, respectively. B. Secretion of phaseolin Δ418. Protoplasts were transformed with phaseolin or phaseolin Δ418. At 24 to 36 h after transformation, protein extracts were prepared from the protoplasts (Cell) and medium (Med). The presence of phaseolin proteins in these protein extracts was detected by western-blot analysis using antiphaseolin antibody. C, Localization of phaseolin in protoplasts of Arabidopsis, tobacco, and bean. Protoplasts derived from leaf tissues of Arabidopsis (At), tobacco (Tb), and bean (Be) were transformed with the phaseolin construct and were fixed 24 to 48 h after transformation. The fixed cells were stained with antiphaseolin antibody followed by fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled anti-rabbit immunoglobulin (Ig) G antibody. As a control for immunostaining, the Arabidopsis protoplasts were treated exactly the same way except that the primary antibody was omitted in g and h. Bar = 20 μm. D, Quantification of the number of discs in a protoplast. The number of the disc as shown in C (a, c, and e) was counted from more than 50 immunostained protoplasts for each plant species. Three identical experiments were performed. E, Localization of phaseolin Δ418. Fixed Arabidopsis protoplasts transformed with phaseolin Δ418 was stained with antiphaseolin antibody followed by FITC-labeled anti-rabbit IgG antibody. Bar = 20 μm. At, Arabidopsis.