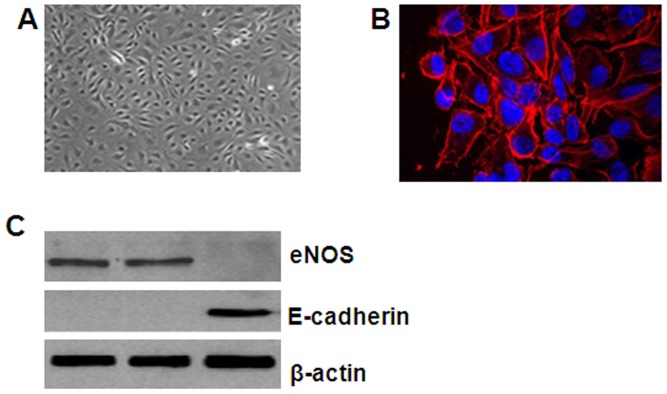
Figure 1. Isolation of lung cancer xenograft-derived ECs.
LLC xenografts were resected from mice injected subcutaneously at the dorsal flank with LLC cells (3×106 suspended in 50 µL PBS) for 30 days. After removing obvious necrotic tissues or extra fatty compositions, the minced tissues were ground on ice using a glass grinder and were then filtered through cell strainers to eliminate tissue debris. (A) The CD31-expressing lung cancer-derived ECs were isolated from the single-cell suspension by immunomagnetic sorting, as evidenced by scanning microscopy, and cultured in vitro. (B) CD31 was detected in the isolated lung cancer-derived ECs using immunofluorescence. CD31 antibody staining of the lung cancer-derived EC membranes is shown in red, and nuclear DAPI staining is shown in blue. (C) Total protein was isolated from enriched lung cancer-derived ECs, bEnd.3 cells (positive control), and MLE-12 (negative control) cells. Western blot analysis was performed using antibodies against eNOS and E-cadherin, and β-actin was used as the internal control.