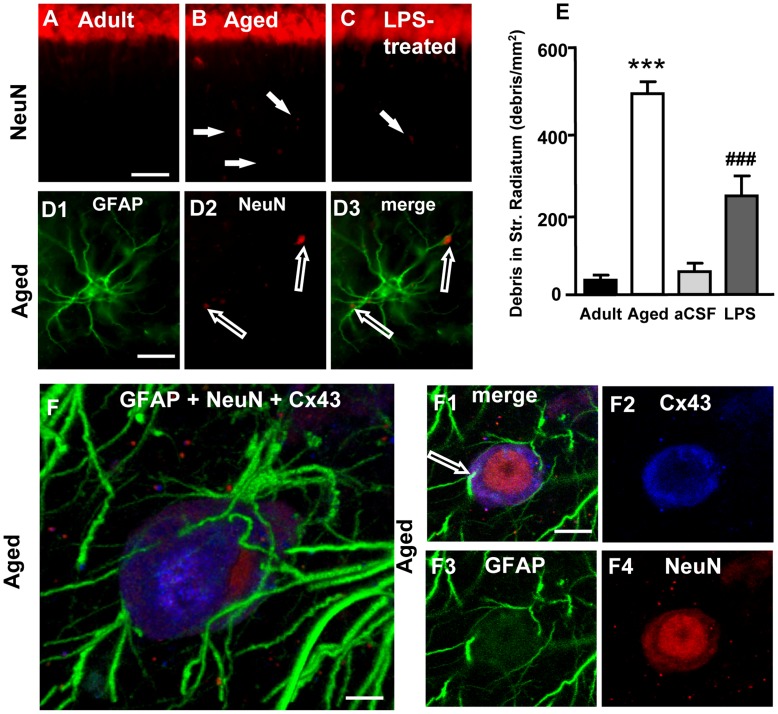
Figure 6. Quantitative analysis of neuronal debris in Str. Radiatum, involvement of Cx43 in astrocytes-neuron interplay.
Images from CA1 Str. Pyramidalis and CA1 Str. Radiatum of an adult (A), aged (B) and LPS-treated rat (C) showing the presence of neuronal debris (arrows, B and C). Scale bar: 70 µm. D1–D3: higher magnification images of GFAP (green, D1) and NeuN (red, D2) staining and the merge of the two previous images (D3). Empty arrows show neuronal debris closely apposed to astrocyte branches. Scale bar: 15 µm. E: quantitative analysis of neuronal debris in CA1 Str. Radiatum of adult (n = 12), aged (n = 10), aCSF- (n = 5) and LPS-treated (n = 6) rats (mean±SEM; *** and ###P<0.001 vs all other groups). F–F4: Representative images of triple immunostaining of GFAP (green), NeuN (red) and Cx43 (blue) in the Str. Radiatum of an aged rat. F: 3D stack of 39 confocal scans (total 14.39 µm); F1: a “sub-slice” of the previous neuron (obtained stacking 6 consecutive scans, total 1.843 µm, starting at a depth of 5.899 µm into the cell) and separate staining of Cx43 (F2), GFAP (F3) and NeuN (F4). Scale bar: 5 µm (F); 10 µm (F1–F4).