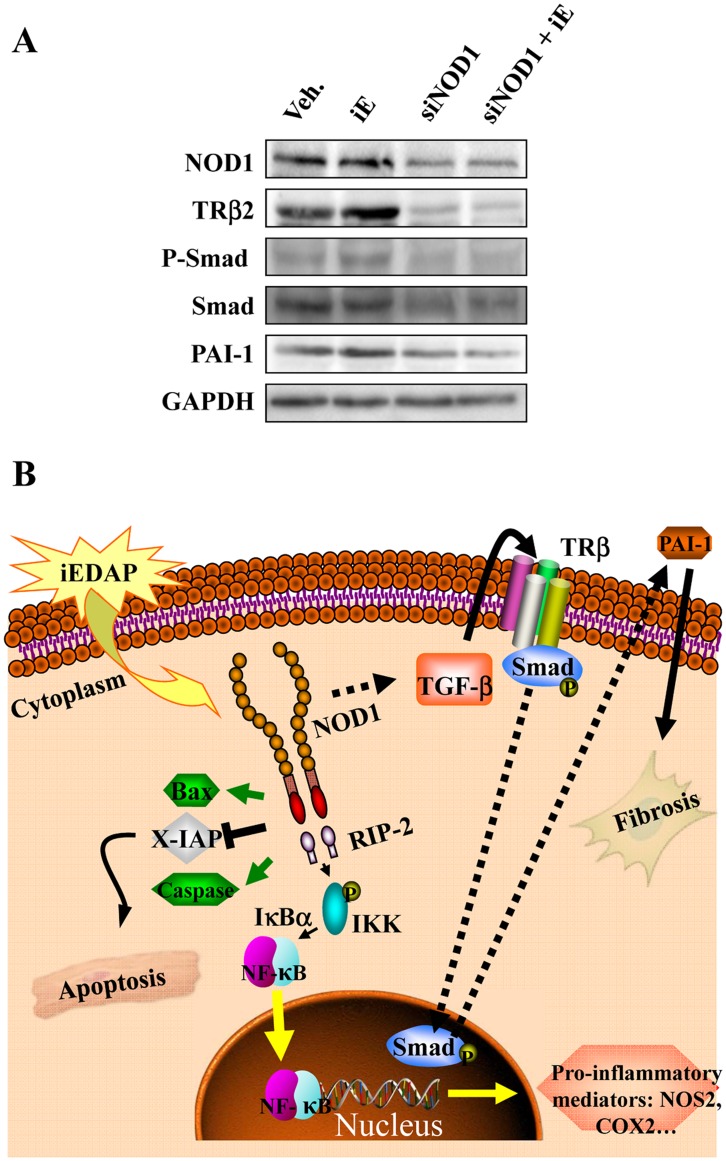
Figure 7. Effect of NOD1 siRNAs on TGF-β pathway. Proposed role for NOD1 activation in cardiac cells.
(A) Representative blot of NOD1, TRβ2, P-Smad/Smad, PAI-1, and GAPDH levels in vehicle, iE, NOD1 siRNAs (siNOD1) and NOD1 siRNA + iE (siNOD1+iE) NIH-3T3 cells. Scrambled siRNA sequences did not modify the basal levels after iE-treatment. (B)The selective agonist iEDAP induces NOD1 activation. Both in cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts, NOD1 promotes the activation of the NF-κB pathway through IKK/IκBα signaling. NF-κB activation induces a proinflammatory response, including the expression of NOS2 and COX2. Moreover, TGF-β is activated in cardiac fibroblasts resulting in PAI-1 transcriptional activation by TRβ and Smad factors. Finally, the enhancement and activation of Bax and caspases and the downregulation of X-IAP promoted by NOD1 agonist in cardiomyocytes, contributes to elicit an apoptotic response associated with NOD1 activation. Altogether, cardiomyocyte apoptosis and the pro-fibrotic profile observed in cardiac fibroblasts might contribute to the onset of cardiomyopathy linked to proinflammatory disease.