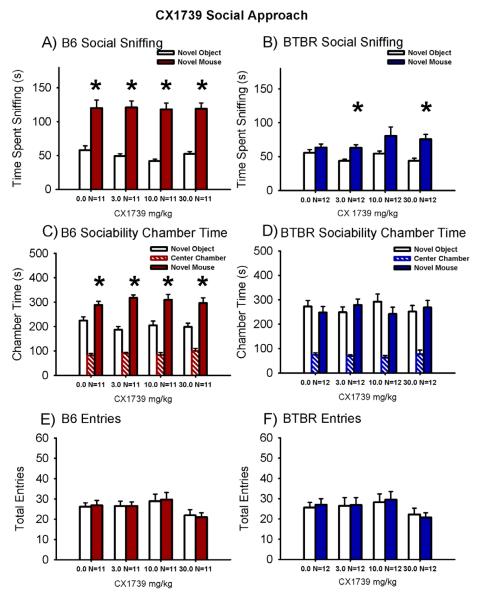
Figure 2. AMPAKINE CX1739 increased social sniffing in BTBR with no deleterious effects in B6 control mice.
An independent cohort of B6 and BTBR mice was tested by a different investigator in the 3-chambered social approach apparatus. (A) B6 treated with CX1739 exhibited its characteristic sociability on the directed sniffing parameter at each dose tested. (B) BTBR exhibited its characteristic lack of sociability, i.e. did not spend more time sniffing the novel mouse versus the novel object, after treatment with peanut butter vehicle. CX1739 at 3.0 mg/kg and 30 mg/kg reversed the usual social sniffing deficits in BTBR on the directed sniffing parameter. A trend toward reversal was observed at 10 mg/kg (p = 0.06). (C) B6 displayed normal sociability on the chamber time parameter, spending more time in the chamber with the novel mouse as compared to the novel object, after CX1739. (D) BTBR exhibited its characteristic lack of sociability on the chamber time parameter following vehicle administration and at each dose of CX1739. No significant difference in the number of entries into the side chambers was observed in (E) B6 and (F) BTBR at any dose of CX1739, indicating the absence of confounding increases or decreases in exploratory locomotion during the social approach task. *p < 0.05, novel mouse versus novel object. N = 11-12 per dose for each strain.