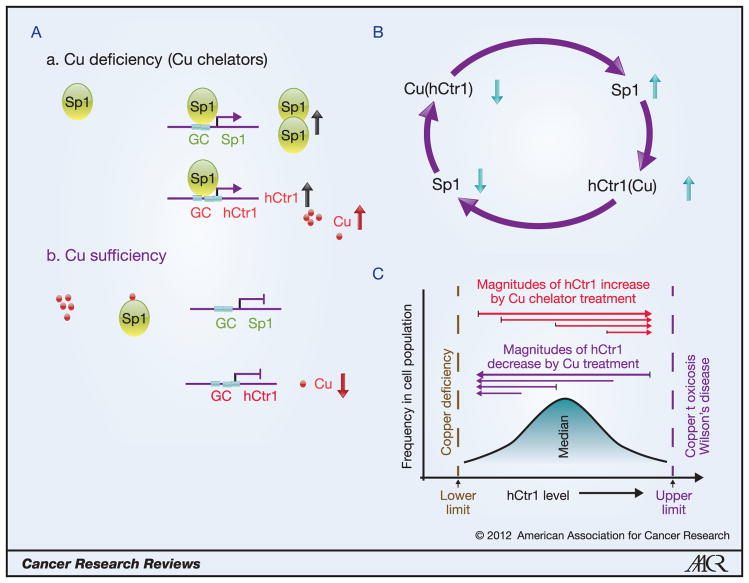
Figure 1.
Regulation of hCtr1 and Sp1 expression by Cu bioavailability. A, Upregulation of Sp1 and hCtr1 expression under Cu deficiency by enhanced promoter binding of Sp1 to these genes (a); Cu sufficiency prevents Sp1 binding to these promoters (b). B, The Cu-Sp1-hCtr1 interregulatory loop for Cu homeostasis regulation. Reducing the Cu levels (downward arrow), either by treating cells with Cu chelators or by expressing the hCtr1 dominant-negative recombinant, upregulates Sp1 and hCtr1 expression (upward arrows); likewise, increasing the Cu levels, either by treating cells with CuSO4 or by transfection with wild-type hCtr1 cDNA, downregulates Sp1 and hCtr1 expression. C, Magnitudes of hCtr1 regulation by Cu bioavailabilities depend upon the intrinsic hCtr1 levels. Low hCtr1-expressing cells exhibit greater magnitudes of hCtr1 induction than do high hCtr1-expressing cells by Cu chelator (red lines); likewise, greater reduction in hCtr1 induction was observed in high hCtr1-expressing cells by Cu treatment than in low hCtr1-expressing cells (purple lines).