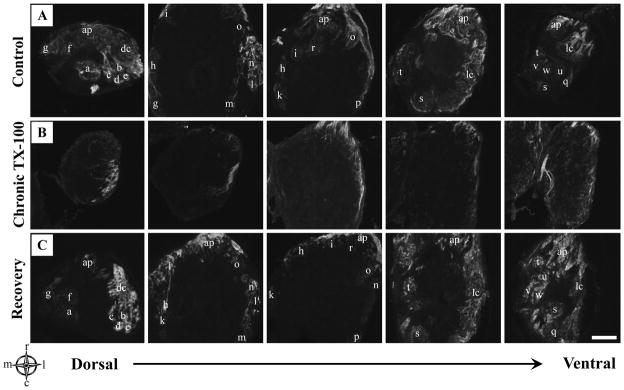
Figure 2.
Anti-KLH immunoreactivity in the olfactory bulb following chronic Triton X-100 treatment and recovery. A) Representative horizontal sections from the dorsal to the ventral regions of control olfactory bulbs stained with anti-KLH showed labeling of all identifiable glomeruli with each glomerulus letter-coded. B) Olfactory bulbs of animals following repeated detergent treatment had noticeably less anti-KLH labeling. The innervation that did remain was most obvious in the lateral regions while the medial region appeared to be affected the greatest. C) Following 3 weeks of recovery, KLH immunoreactivity seemed to return to control levels, with glomeruli present in all regions of the olfactory bulb. Glomeruli were letter-coded in control olfactory bulbs as follows: a=dcaG1 (dorsal-cluster-associated glomeruli), b=dcaG2, c=dcaG3, d=dcaG4, e=dcaG5, f=mdpG1 (mediodorsal posterior glomeruli), g=mdpG2, h=mdG (mediodorsal glomerulus), i=maG (medioanterior glomerulus), k=meG (medial elongated glomerulus), l=lcG1 (glomeruli of the lateral chain), m=lcG2, n=lcG3, o=lcG4, p=lcG5, q=lvpG (lateroventral posterior glomerulus), r=vaG (ventroanterior glomerulus), s=vpG (ventroposterior glomerulus), t=vmG (ventromedial glomerulus), u=vtG1 (glomeruli of the ventral triplet), v=vtG2, w=vtG3, dc=dorsal cluster glomeruli, ap=anterior plexus. For compass, m=medial, l=lateral, r=rostral, c=caudal. Scale bar = 100μm for all.